
Читайте также:
|
BASIC CUISINE
KNOWLEDGE
FOR
KITCHEN PRACTICALS
* KAZAKHSTAN *
CHEF: Frédéric
 |  |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TOPIC:PAGE:
Kitchen work flow…………………………………….….……..3 - 4
Hygiene & Safety in the Kitchen………………………….…....5 - 8
Basic Equipment Identification…………………..….………...10 - 19
Classification of fruits and vegetables…………………………20
Basic Methods of Vegetables Cutting………………..………...21 - 23
Methods of Preparing Potatoes………………………..……….24 - 28
Methods of Cooking……………………………………......…..29 - 37
Basic Stocks, Roux and Sauces………………………….……..38 - 46
 Book References………………………….…………………..…47
Book References………………………….…………………..…47
 |  |
TRADITIONAL CONCEPT OF KITCHEN WORK FLOW
The whole production is realized in the cooking area from raw materials. This concept needs the setting and the application of the logical and the rational process called “forward flow”. It uses numerous specific areas and a highly qualified staff.
| GOODS RECEPTIONS *Qualitative and quantitative control of goods received | · Elimination of crates, boxes. The different foodstuffs are disposed in special plastic containers with lids easily disinfected. · Remove packaging according to the nature of the products. |
| STORAGE *Goods storage before preparation with specific temperature. *Dry store *Freezer *Chiller | · Dry goods:+15°C To +18°C · Chilled meats: 0°C to +3°C · Chilled poultry: 0°C to +4°C · Chilled fish: 0°C to +6°C · BEC(Dairy products:+6°C · Fruits or vegetables=+6°C to +10°C (except tropical fruits) · Potato and roots=Cold area without light and protected against insects and rodent |

| PRELIMINARY PREPARATIONS *Specific areas(vegetable, butchery and larder) | · Peeling, washing and cutting. · Fish and dressing of chicken · Game preparation · De-boning and meat preparation |
| COOKING OR PREPARATION OF DISHES * Hot kitchen *Cold kitchen or larder(Garde manger) *Pastry kitchen or bakery | · The different preparations are organized and carried out under the respective department chefs according to meal service times. |

| DISTRIBUTION(SERVING) *Control portioning *Check finishing | · Dishes are served to guests |
KITCHEN PREMISES

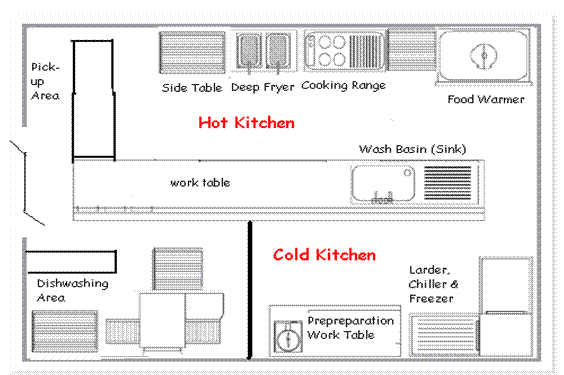
It is important to have proper planning of the layout of a commercial kitchen. This is to ensure that daily operations run efficiently. The diagram above shows an example of a kitchen layout that emphasizes on ‘ forward flow ’.
Below is an example another example of a kitchen layout in a restaurant and allocation of equipments:
HYGIENE AND SAFETY IN THE KITCHEN
- Micro-organisms & Food poisoning:
► Food poisoning or food borne illness is a general term applied to diseases which result in a disturbance of gastrointestinal tract, normally affecting the stomach and intestines.
ð Pathogenic Bacteria. We shall call them harmful germs.
ð The three most common are:
* Salmonella (80% of food poisoning caused by salmonella),
* Clostridium Perfringens,
* Staphylococcus Aureus.
They are microscopic. This means we can not see them with the naked eye. Contaminated food may therefore look the same as fresh food; it can also taste and smell normal.
- Sources of germs:
► Raw food,
► Humans,
► Animals and birds,
► Insects (flies and cockroaches),
► Soil and dust.
- Factors having an influence on the growth of bacteria:
- Time
- Moisture
- Warmth
- Food
If just one of the four factors required for growth is removed, the germs will not be able to multiply and the food will be safe
Personal Hygiene
· Wash hands with soap before working with food but also after entering toilet, after smoking, after blowing your nose, after handling raw food, after eating, throughout the work day.
· Do not wear excessive jewelry.
· Use a fork/spoon for tasting or sampling of food.
· Keep hair and nails short and/or well trimmed. Ladies with long hair should tie their hair neatly and if possible tucked under cook’s hat.
Uniform
· Chef’s Jacket: clean, buttoned and ironed.
· Chef’s Scarf: neatly knotted.
· White Apron: clean and pressed (ironed).
· Cook’s Hat: neatly covering hair.
· Side Towel: clean and dry.
· Chef’s Pants: proper length.
· Safety Shoes: clean and properly fitted.
Before entering the kitchen, all kitchen staff should be in full uniform. Ensure that you do not wear prohibited jewelries which may endanger yourselves or others either by cross-contamination or getting entangled with heavy equipments. Also, keep hair and nails well-trimmed at all times. For men, make sure that face is well-shaven. All these regulations are meant to encourage discipline, hygiene and safety amongst food professionals. The following is a pictorial illustration of the said regulations:

Handling of Knives and Cooking Utensils
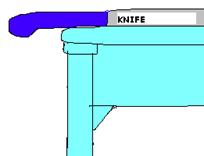
Knives are to be carried with respect and in the safest position possible. The following illustrates the proper and improper ways of carrying a knife while moving around the kitchen.
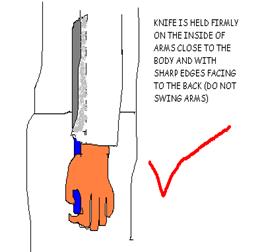

One must learn to grip a knife correctly while cutting or chopping. The proper slicing movements are also crucial for efficient cutting.

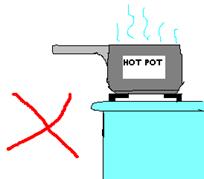
Do not leave knives on uneven surfaces or partially protruding (over the edge) of work surface. Accidents might happen if it is knocked over. This also applies to handles of pots and other sharp objects.
Oil spills
Oil spills may cause slippage and accidents. During busy hours on high traffic areas, sprinkle lots of salt on affected area to create friction. During off-peak periods, rinse with boiling hot water and dry immediately (use of detergent is also encouraged) 
General Rules
· Observe safety rules while working with sharp knives and other equipment.
· Keep your work station clean. You are responsible for washing your own equipment.
· Use clean utensils and equipment.
· Use separate cutting boards and equipment for raw and cooked food and vegetables.
· Each student is responsible for general housekeeping of the kitchen.
· Inform your instructor of any physical disabilities that might cause danger to you or another student while you work in the kitchen.
· Never sit on any piece of equipment including worktables.
· Return all equipment to its proper location.
· All students should be in full uniform and be punctual for practical classes (preferably at least 15 minutes before class commences).
· DO NOT wear your kitchen uniform outside of school premises.
Tools
· Knife set: knives must be sharpened at all times.
· Peeler: for peeling of vegetables and fruits.
· Food Tongs: for handling of food without hand contact.
· Spoons: for tasting / sampling food.
· Water Bottle: DO NOT use glasses in the kitchen for drinking water.
Kitchen Conduct & Safety
· Do not share the same cutting board. One cutting board per student.
· Do not use a blunt knife for cutting.
· Handling of equipment must be by one person at a time only.
· Keep noise levels low as much as possible.
· Always warn others in the way when carrying hot / sharp objects.
· Practice proper ways of holding knives especially when moving around the kitchen.
· Do not use a knife to point at a person nor direction. Put knife down first.
· Do not throw broken glasses / plates into dustbins. Always report breakages to your instructor.
· Dress wounds properly and if possible, wear a glove.
· Do not bend your back when lifting heavy objects. Instead, bend your knees and keep your back straight.
· During busy periods, if an oil spill occurs, sprinkle with a lot of salt to increase friction and avoid slips. Clean with detergent and hot water later.
· Do not leave pot handles sticking out when a passer-by may accidentally knock into it.
· Never physically fool around in the kitchen.
· If in a hurry, walk fast. Do not run.
· Make it a habit to use your side towel when handling hot equipments.
· Do not use a wet towel to handle hot items as the steam from the towel will scald your hand.
· ASK, ASK and ASK whenever you are unsure of any practice / usage of equipment.
· REMEMBER: “It is your duty to keep your body parts intact and well throughout your practicals here in TCHT!
EQUIPMENT:
It is legal requirement that equipment with which food comes into contact is kept clean and kept in such good order, repair and condition to enable it to be effectively clean.
Kitchen equipments is expensive so initial selection is important.
The following points should be considered before each item is purchased or hired:]
Kitchen equipment may be divided into three categories:
LARGE EQUIPMENTS/MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT:
| EQUIPMENT | FUNCTIONS | REMARKS |
| 1.STOVE/OPEN BURNER | For cooking. | |
| 2.SALAMANDER | To gratinate food or to melt and brown cheese. The heat came from the above. | |
| 3.MICROWAVE OVEN | For heating food in a fastest way. | |
| 4.MIXER | Very important in pastry preparation. To mix dough: Example in making bread dough, short crust pastry or and other dough. | |
| 5.DEEP FRYER | To deep-fry items. Usually when frying large amount of the items | |
| 6..HOT PLATE | Use for glazing or when prepare reduction method of cooking. | |
| 7..BAIN MARIE | To keep food warm. Method of heating up is by using hot water. | |
| 8..DECK OVEN | Usually use for baking pastry items. | |
| 9.WORKING STATION | The place where the kitchen personnel work. | |
| 10..SINK | Washing vegetables and equipments. | |
| 11..PICKUP AREA | Last –lace where food is being check by the aboyer before food is being pickup by the server. | |
| 12..HOT WATER BOILER | Boiling hot water | |
| 13..TABLE FRIDGE | Necessary to keep all the unused items. Especially all the perishable items. | |
| 14..EXHAUST HOOD | To extract all the smokes. Maintain a good air circulation. | |
| 15..WALK IN CHILLER | To keep all the chill items. Temperature is 0oC to 5oC | |
| 16..DISHWASHING MACHINE | To wash plates and cutleries | |
| 17..POT WASHING AREA | To wash pots and pans. | |
| 18.COMBI OVEN | A combination oven use for baking, roasting and steaming. | |
| 19.GRILLER | Is an under fired stimulated charcoal grill or cast iron grid. The food is cook on the bar which giver extra flavor by the hot fat dripping from the food. The fire is from below. | |
| 20.GRIDDLE | Solid plates heated from below. The plates are covered with cast iron. Usually use for frying eggs making burgers and pancake.etc. |
(See table below p.11, 12, 13)
UTENSILS AND SMALL EQUIPMENTS
| NAME OF THE EQUIPMENT | FUNCTIONS | REMARKS |
| 1. STOCK POT | To prepare stock | |
| 2.SAUCE POT | To prepare sauce | |
| 3.WIRE WHISK | To whisk soft items like cream and eggs | |
| 4.METAL SPATULA | Spread toppings on cakes. Use to flip over pancake | |
| 5.SOUP LADDLE | To scoop soup | |
| 6.SAUCE LADDLE | To scoop sauces | |
| 7.SKIMMER | To skim the scum To lift up items from poaching liquid or frying oil. | |
| 8.WOODEN SPOON | To stir.During the process of cooking. | |
| 9.FOOD TONG | To pickup food items. | |
| 10PLASTIC SPATULA | For scraping. | |
| 12.ROLLING PIN | To flatten dough | |
| 13.CHOPPING BOARD | Use for cutting or chopping an items | |
| 14.CHINA CAP | Use for straining Example: Soup and sauces | |
| 15.MIXING BOWL | Multi purpose. Example use for: Mixing salad, making of cold sauces Very important equipment use for the food Preparation. | |
| 16.TURN TABLE | Important in dessert preparation. For event spreading of cakes topping | |
| 17.FISH SCALLER | To remove fish scales | |
| 18.TART MOULD | To prepare tart sweet or savory | |
| 19.MANDOLINE | For slicing vegetables in different way of shape and sizes | |
| 20.COLLANDER | More useful in draining of vegetables and pasta. | |
| 21.BOX GRATER | Used to grate cheese, eggs and potatoes. | |
| 22.BAKING TRAY ROASTING TRAY | Used for baking or roasting | |
| 23.DARIOLE MOULD | Making pudding, mousses and bavaroise. | |
| 24.SAUCE BOAT/ALADDIN | To put sauces and dressing. | |
| 25.CAN OPENER | To open canned foods. | |
| 26.FLAN RING | To prepare fruit flan or tarts. | |
| 27.CAKE MOULD | To mould cakes in various shape | |
| 28.WEIGHING SCALE | To weigh solid items. | |
| 29.MEASURING JAR | To measure liquid items | |
| 30.ICING BAG@NOZZLE | Used in pastry and dessert preparation. Example making of roses and lining of cakes. | |
| 31.PASTRY BRUSH | Mainly used for pastry preparation. Use for glazing bread and greasing cake mould with fat in order to prevent from sticking. | |
| 32.TARTLETTS MOULD | To prepare tarts. | |
| 33.DOUGH CUTTER | To cut dough or to portion dough to the required amount. | |
| 34.SILVER PLATTER | Used for serving or putting Mise en place. |
(See table below p.14, 15, 16)
BASIC EQUIPMENT IDENTIFICATION
 SKIMMER
SKIMMER
|  CHINA CAP
CHINA CAP
|  WOODEN SPOON
WOODEN SPOON
|
 LADLE
LADLE
|  WIRE WHISK
WIRE WHISK
|  MIXING BOWL
MIXING BOWL
|
 COLANDER
COLANDER
|  FOOD MILL
FOOD MILL
|
 MANDOLINE MANDOLINE
|
 STOCK POT
STOCK POT
|  SAUCE POT
SAUCE POT
|  SAUTE PAN / FRYING PAN SAUTE PAN / FRYING PAN
|
 SAUCE PAN SAUCE PAN
|  ROASTING PAN ROASTING PAN
|
 COOKING RANGE
COOKING RANGE
|  DEEP FRYER
DEEP FRYER
|
 FOOD PROCESSOR FOOD PROCESSOR
|  TABLE MIXER TABLE MIXER
|
 SLICER SLICER
|  JUG BLENDER JUG BLENDER
|
 SALAMANDER
SALAMANDER
|  GRIDDLE
GRIDDLE
|

|

| ||||
 COMBINATION OVEN
COMBINATION OVEN
|  DISHWASHER
DISHWASHER
|
Identification of Knife Parts
| 1. Point Function: the piercing tool of the blade 2. Tip Function: cutting small delicate foods, boning, filleting 3. Edge Function: slicing 4. Spine Function: strengthening of blade 5. Heel Function: cutting or chopping large or tough foods. Eg. Bones 6. Bolster Function: only found on forged knives Balancing of knives Protect hand from blade 7. Tang Function: balancing of knife Strengthening of whole knife especially between Handle and blade 8. Scales Function: grip of handle 9. Butt Function: end of handle | 
|
IDENTIFYING THE VARIOUS TYPES OF KNIFE

Paring Knife: Peeling, slicing small fruits and vegetables, removing stems and other
Small cutting tasks where control is essential

Turning Knife: cutting curved surfaces or”tournee” vegetables

Utility Knife: Slicing small pieces of meat, cold cuts, fruits, carving poultry

Chef’s Knife (French Knife): All-purpose, chopping, slicing, mincing

Boning Knife : Deboning of meats and poultry

Filleting Knife : Flexible and ideal for removing skin and bones from fish

Bread Knife (Serrated Knife): Slicing food with tough skin or crust

Slicer: Slicing boneless cooked meats, poultry and fish
IDENTIFYING THE VARIOUS USTENSILS OF THE KNIFE SET

| 
| PASTRY BRUSH: Mainly used for pastry preparation. Use for glazing bread and greasing cake mould with fat in order to prevent from sticking. Also to egg-wash food surface. |

| 
| SPOON: Mainly use to taste the food, or stir some preparation, but make sure that your spoon is clean and always with you. It can be kept in a small container filled with water. |

| 
| PLASTIC SPATULA: Can be used for stirring or scraping sauce from a bowl or pan. DO NOT USE ON VERY HOT SURFACE: MELT |

| 
| METALLIC SPATULA: Uses range from “flipping” food to applying creams, butter, icing on surface of food. Also a tool in chocolate crafting. |

| 
| SCRAPER: Assist in handling cream, batter or dough. |

| 
| TRUSSING NEEDLES: Mainly use during the trussing of the poultry where a string is attached to one end with the purpose of “tying” to maintain a presentable shape while cooking. |
Holding a knife with a proper grip
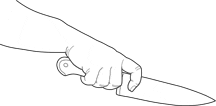
Grip the knife around its bolster. The bolster is both your knife's balance point and a finger guard. Only your last three fingers should rest on the handle. Your thumb and index finger should be on opposite sides of the blade. When you hold a knife around its balance point, it works as an extension of your hand. Hence your arm doesn't tire and you have excellent control.
Use your guiding hand when cutting
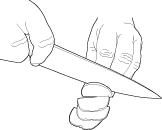 Whether it's dices, julienne cuts, or straight slices, your other hand has a key role to play. It stabilizes the food you are cutting, guides the knife, and determines the size of your cut. Make certain that your fingers are curled inward and your thumb is tucked underneath. The side of the blade should rest against your knuckles, but NEVER the edge itself. Remember to take it slowly at first. It is all about technique.
Whether it's dices, julienne cuts, or straight slices, your other hand has a key role to play. It stabilizes the food you are cutting, guides the knife, and determines the size of your cut. Make certain that your fingers are curled inward and your thumb is tucked underneath. The side of the blade should rest against your knuckles, but NEVER the edge itself. Remember to take it slowly at first. It is all about technique.

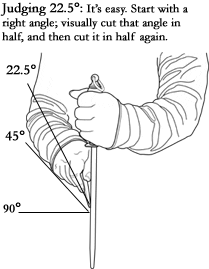
Using a Sharpening / Butcher’s Steel
VEGETABLES
The term vegetable in common usage has come to include any edible parts of any plant.
Vegetables may be roots, tubers, stem, bulbs, flowers, seeds, leafy and etc.
| NO | CLASSIFICATIONS | EXAMPLES |
| GREEN AND LEAFY |
| |
| FLOWER/BRASSICA |
| |
| PODS AND SEEDS OF LEGUMES GREEN VEGETABLES |
| |
| FRUITS |
| |
| STEMS |
| |
| ROOTS |
| |
| TUBERS |
| |
| BULBS |
| |
| 9. | FUNGI |
|
VEGETABLES: Basic Cutting
| NAME | SIZE | USAGE | ||||||||
| STICK |   1.Julienne 1.Julienne
| Very thin strips | For garnishing dishes | |||||||
 2.Jardinière 2.Jardinière
| 4 cm x 4mm x 4 mm | Condiments or side dish for main course | ||||||||
| DICE |  3.Brunoise 3.Brunoise
| The smallest dice 3 mm x 3mm | Garnishing for soup usually doesn’t need to be cook | |||||||
 4.Macedoine 4.Macedoine
| 0.5 cm x 0.5 cm | For salads ex. Macedoine mayonnaise | ||||||||
 5.Mirepoix 5.Mirepoix
| 1 cm x 1 cm cube or roughly dice | For deglazing ex. To make roast gravy or making of stock (aromatic garnish) | ||||||||
 6.Paysanne 6.Paysanne
| Thin square or triangle | For soup ex. Vegetable soup | ||||||||
 Ä Stick
Ä Stick
  
 Batonnet / Jardiniere Batonnet / Jardiniere
Ä Dicing:
LEAVES: Basic Cutting
| ||||||||||
| CHIFFONADE (Refer to cabbage or lettuce) | Roll into cigar and julienne | Usually finely shredded of lettuce and stewed in butter | For garnishing soup | |||||||
| BULBS: Basic Cutting | ||||||||||
| REFER TO ONIONS or SHALLOTS | Chop | For onions or garlic | For sautéing | |||||||
| Slice | Very thin cut, usually for onion or other type of vegetable | Making soup or garnishing tarts | ||||||||
| Rings | Usually refer to onion | Use for garnishing | ||||||||
| OTHER VEGETABLES: Basic Cutting | ||||||||||
| Wedges | Refer to tomatoes, lemon and eggs. | Usually for garnishing salads or main course | ||||||||
| REFER TO TOMATOES | Tomato Concasse | Tomatoes usually blanched, refreshed, seeded and chopped. | Use for many purposes such as garnishing for sauces or accompaniments. | |||||||
| Tomato Fondue | Cooked tomato concasse. | To accompany pasta, fish, etc. | ||||||||
| REFER TO GARLIC | Garlic | Chopped or crushed | Use for cooking stew | |||||||
ð Chopping Onions & Shallots (Ciseler)





ð Chopping Parsley and Other Herbs (Hacher)



ð Chiffonade (finely shredded) for leaf vegetables only



ð Mirepoix (rough cuts of vegetables) for flavoring stocks, soups and dishes












POTATOES: Basic Cutting
(Deep fried)
| STICK |  1.Pont neuf (new bridge) 1.Pont neuf (new bridge)
| Refer to potato cut into stick 7 cm X 1 cm. | Accompaniment or side dish for main course (deep-fried) | |
 2. Pomme mignonette (cute) 2. Pomme mignonette (cute)
| Refer to potato cut into stick 5 cm X 0.5 cm. | Accompaniment or side dish for main course (deep-fried) | ||
 3. Pommes Allumette (matchstick) 3. Pommes Allumette (matchstick)
| Refer to Potato cut into stick 5cmX3mm. | Accompaniment or side dish for main course (deep-fried) | ||
 4. Pomme paille (straw) 4. Pomme paille (straw)
| Refer to potato cut into stick 5 cm X 2 mm. | Garnishing for dishes and salads (deep-fried) | ||
 4. Pomme cheveux (hair) 4. Pomme cheveux (hair)
| Refer to potato cut into very fine strips | Garnishing for dishes and salads (deep-fried) | ||
| SLICE | * Gaufrette potato (wafer) * Chips potato | * Slicing into waffle shape by using mandolin. * Thin slice | Accompaniments for main course such as roasted duck. | |
| BOILED potato | ||||
| MASHED | Pommes puree | Boiled potato and mashed | Accompaniments for main course such as beef stroganoff or fish. | |
 |
Pommes Cheveux:
J Potatoes are peeled, sliced thinly to 1mm and cut to fine straws.


 Pommes Paille:
Pommes Paille:
J Potatoes are peeled, sliced thinly to 2mm thickness and cut to fine straws.









 Pommes Gaufrette:
Pommes Gaufrette:
J Potatoes are peeled. Using a mandoline, the potatoes are sliced using the “crinkled” blades set at 2 mm thickness, alternating 45 degrees angle to the left and then right to obtain the “waffle-like” shapes.
 |  | ||||
 | |||||
Pommes Allumettes:
J Potatoes are peeled, cut into matchsticks which are 3mmx3mm in width.
 |  | ||||
 | |||||
Pommes Mignonettes:
J Potatoes are peeled, cut into batons of 6mm x 6mm in width.
 | |||
 | |||
Pommes Pont-Neuf:
J Potatoes are peeled, cut into batons of 1 cm x 1 cm in width.
TURNING POTATOES

| 
|
| Cut the edges off the potatoes | On each side |

| 
|
| Cut the potatoes in two length-wise | Or in four depending on the size of the potato and the shape. |

| 
|
| Cut the potato to produce “oblongs” starting from one side going to the other one. | First try to start with the flat side |

| 
|
| Then the rest of the potatoes | |

| 
|
| Do one cut and turn the potato after each cutting | After few cutting you can see the round shape coming out (like an egg) |

| 
|
| After, just do the finishing | And you get a nice turning potato with 7 sides. |

|
 Ä Most of the turn potatoes are cooked using the RISSOLER method:
Ä Most of the turn potatoes are cooked using the RISSOLER method:
 ð TURNED POTATO
ð TURNED POTATO
 ð BLANCH with cold water (few minutes depending on the size of the potato)
ð BLANCH with cold water (few minutes depending on the size of the potato)
 ð PAN FRIED (until light brown color)
ð PAN FRIED (until light brown color)
ð OVEN 180°C (until full cooked)
 **** Pomme Fondante: ****
**** Pomme Fondante: ****
 | |||
 | |||
· Potatoes are turned to size of a “soap bar” app. 90 g.
· Melt some butter in a pan and place blanched potatoes.
· Season with salt and moisten with some white chicken stock.
· Cover with greaseproof paper and place in oven set at 160 C for about 60 mins (turning the potatoes a few times during cooking and adding chicken stock if necessary).





 * Pomme Vapeur & Pomme à l’anglaise:*
* Pomme Vapeur & Pomme à l’anglaise:*
· Potatoes are turned to “barrels” of 7cm length and 4.5 cm in diameters.
· Potatoes are steamed for pomme vapeur or boiled for pomme à l’ anglaise. Normally served with fish.
 |






 **** Pomme Château: ****
**** Pomme Château: ****
· Potatoes are turned to “barrels” of 6 cm length and 3.5 cm in diameters.
· Cooking method is Rissoler.
 | |||||||
 |  | ||||||
 | |||||||
**** Pomme Cocotte: ****
· Potatoes are turned to “oblongs” 6 cm length and 2 cm in diameters.
· Cooking method is Rissoler.

 **** Pomme Noisettes: ****
**** Pomme Noisettes: ****
·  Potatoes are shaped into “hazelnuts” using a parisienne scoop (melon baller).
Potatoes are shaped into “hazelnuts” using a parisienne scoop (melon baller).
· Cooking method is Rissoler.
* HEAT TRANSFER *
Ø In order to cook food heat must be transferred from heat source to and through the food.
Ø Understanding how heat transfer during cooking help cooks to control cooking process.
 3 WAYS OF HEAT TRANSFER
3 WAYS OF HEAT TRANSFER
1. CONDUCTION
Ø Heat moves directly from top of the ranges to pot and to the broth inside.
Ø Heat moves rapidly through copper and aluminum but slowly through stainless steel.
2. CONVECTION
Ø Happens when movement of air, steam or liquid spreads heat.
“ TWO KINDS OF CONVECTION “
Natural
Ø  When pot of liquid being heated up the hot liquid will rise up and the cooler area of liquid will sink to the bottom.
When pot of liquid being heated up the hot liquid will rise up and the cooler area of liquid will sink to the bottom.
Ø Circulation of heat happens.
Ø When its starts bubbling the whole liquid will become hot.
Ø It doesn’t need stirring.
Mechanical
Ø It happens in convection oven and convection steamers.
Ø Fan in the oven spread the circulation of heat in the oven.
Ø As a result heat transfer more quickly to the food.
Ø Stirring is a form of mechanical convection.
Ø In thick liquid rate of natural convection is slower.
Ø Stirring manually in thick liquid is also to prevent from scorch.
Ø By using heavy pots made of material that conducts heat well also helps scorching happens.
Ø Pots conduct heat more quickly and evenly all across the bottom and up the side.
3. RADIATION
Ø Energy transferred by waves, from the source to the food.
Ø Microwaves cook rapidly; they will not break the connective tissue of less tender meat. Slow moist cooking is necessary for dissolving this connective tissue.
“ TWO KINDS OF RADIATION “
Infrared
Ø Heat is generated from electric element
Microwave
Ø Radiation generated by the oven to penetrate into the food.
Ø Microwave radiation effects only water molecules.
Ø Friction cause by agitation creates heat that will cook the food.
* THREE FACTORS AFFECTING COOKING TIME *
1. COOKING TEMPERATURE
Ø Air in the oven
Ø Fat in the fryer
Ø Liquid in which food is being cook.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-29; просмотров: 128 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| edit] Electric machines | | | SIZE, TEMPERATURE AND CHARACTER OF FOOD |