
|
Читайте также: |
Table of Contents
1. Introduction……………………………………………………….2
2. Background Information………………………………………3
2.1 Diabetes the Disease (Defined)……………………3
2.2 Cause of Diabetes……………………………………4
2.3 Diabetes and Aboriginals…………………………..6
3. Current Situation……………………………….…………….….7
3.1 Analysis of issues confronted by Aboriginals……...7
3.2 Effect of Diabetes on Aboriginals/Communities….8
4. Current Management Strategies………………………...…....9
4.1 Medical Strategies……………………………………..…9
4.2 Social Strategies……………………………………….....9
5. Proposed Strategies to Manage Diabetes for Aboriginals..10
5.1 Decision Making-Matrix………………………………..11
5.2 Evaluation of Proposals…………………………………12
6. Recommendations………………………………………………...14
7. Conclusion………………………………………………………….15
8. Bibliography/ Reference List…………………………………..16
9. Appendix…………………………………………………………….17
Introduction
Diabetes affects nearly 1 million Australians with many of these people being unaware that they have the disease. Type 2 Diabetes is a major contributor to indigenous mortality, being responsible for almost 8% of deaths of Indigenous people living in QLD, WA, SA and the NT in 2002-2006.
This report will investigate the following main points:
Ø Background information on the disease;
Ø The current situation of the type 2 diabetes disease;
Ø Current strategies in preventing and managing diabetes among Indigenous Australians;
Ø Two disease management proposals will be analysed and evaluated to ascertain the most viable solution to managing the disease
This report will recommend a viable option to more successfully provide primary health care for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people who are suffering from diabetes. The options will be assessed against 3 criteria to ascertain their overall effectiveness.
Background information
Diabetes the Disease
Diabetes is a chronic condition which sometimes causes death.
Diabetes mellitus is a condition where the body cannot maintain normal blood glucose levels. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose move from the blood into the cells. When the body does not produce enough insulin, the blood glucose level rises (Healthinsite, 2012). Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the most common among Indigenous population.
Type 1 diabetes is marked by a total or near-total lack of insulin. It results from the body destroying its own insulin producing cells in the pancreas. It's an autoimmune condition not primarily caused by lifestyle factors and is one of the most common chronic childhood diseases (although it can occur at any age). It's characterised by a typically rapid onset and symptoms can include excess thirst and urination, unexplained weight loss, irritability, weakness and fatigue. People with this form of diabetes require daily insulin injections to survive
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form and cases are rapidly increasing. It currently accounts for 85–90% of all cases of diabetes. It's marked by reduced levels of insulin (insulin deficiency) and/or the inability of the body to use insulin properly (insulin resistance) and its onset is usually slow and in older adults over the age of 30 but may occur in overweight teenagers and children with a family history of diabetes.
Type 2 is often diagnosed by routine blood tests and there are often no typical symptoms. But when blood glucose reaches higher levels, symptoms can include excessive thirst and urination, weakness and fatigue, blurred vision, infections that don't heal or heal slowly, tingling and numbness in the feet. It's typically treated by keeping healthy weight, healthy eating and regular exercise.
Diabetes is a major health concern due to the significant complications including increased risk of heart disease and stroke, blindness, kidney failure, limb amputation, and erectile dysfunction in men. See Appendix Figure 2.
It is estimated that one million Australians have diabetes and about half of those even are not aware that they have the condition.
Causes of Diabetes
The best way to manage the onset of diabetes is to know the risks which cause this disease. This information should be provided by health organisations, and should be spread all over the schools, hospitals and especially in Indigenous communities. This will lead to rise of literacy rate, so people will be able to prevent themselves from such a chronic disease as Diabetes.
”Generally, the risk of developing diabetes increases with age. The disease can also affect women during pregnancy, leading to complications for both mother and child, this is known as Gestation Diabetes. Certain population groups, notably indigenous Australians and some ethnic groups, have higher rates of diabetes. Many cases of type 2 diabetes could be prevented or delayed through simple lifestyle changes that lower the risks of diabetes and other chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer. These risks include excess weight, poor diet, inactivity, smoking and too much alcohol (Healthinsite, 2011).”
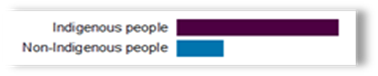 Referencing to figure 1, diabetes is more common in Indigenous Australians than in non-Indigenous Australians
Referencing to figure 1, diabetes is more common in Indigenous Australians than in non-Indigenous Australians
Figure 1. The proportion of people with diabetes in the non- Indigenous population. (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2012)
Figure 2, Multifactorial model clearly outlines the pathways to Type 2 Diabetes in an indigenous population. Geographical isolation, low socioeconomic status, as a result poor diet and poor access to health care services cause the chronic disease amongst Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. So there are a lot of factors which cause this disease among indigenous population, this information will help to manage outlined factors and prevent Type 2 Diabetes.
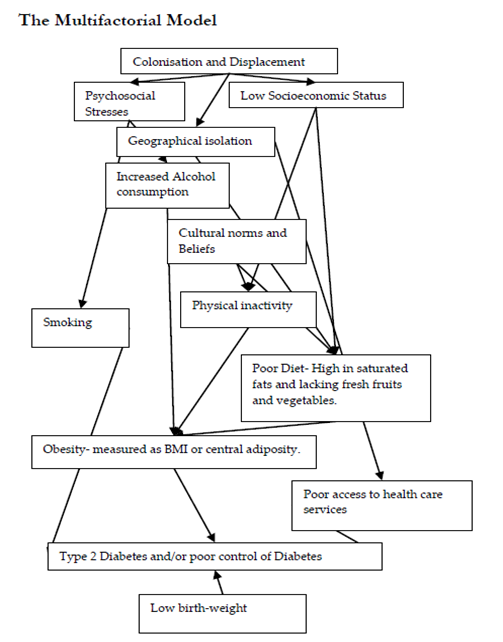
Figure 2. A Multifactorial Model listing out the pathways to Type 2 Diabetes in an indigenous population (Shukla, 2010).
Дата добавления: 2015-10-29; просмотров: 111 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Пол Галлико | | | Analysis of issues confronted by Aboriginals |