
Читайте также:
|
E. No right answer
23. Consider two constant-average-cost industries (#1 and #2) with linear market demand functions, which are exactly the same in everything except:
- industry #1 is perfectly competitive
- industry #2 is monopolized
The government introduces a per-unit subsidy of $1 for both industries. How will this affect the price paid by buyers of those industries?
A. #1 – increase by $1; #2 – increase by more than $1;
B. #1 – decrease by $1; #2 – decrease by less than $1
C. #1 – decrease by less than $1; #2 – increase by less than $1
D. #1 – increase by $1; #2 – increase by less than $1
E. #1 – decrease by $1; #2 – decrease by more than $1
24. The following graph illustrates a firm in the situation of long-run equilibrium.

Judging from this graph, which market structure could that firm operate in?
A. A perfectly competitive market
B. A monopolistically competitive market
C. A discriminating monopoly
D. A natural monopoly
E. Several answers are correct
25. Suppose there are two firms in an industry. There are three alternatives available to each firm: (A) invest in both quality and advertizing, (B) invest in advertizing only and (C) invest in cost reduction. The firms simultaneously choose their strategy. All possible payoffs are given by the following matrix:
| Firm 2 | ||||
| Firm 1 | A | B | C | |
| A | 0,5, 0,5 | - 1, 1 | 1, -1 | |
| B | 1, - 1 | 0,5, 0,5 | -1, 1 | |
| C | - 1, 1 | 1, - 1 | 0,5, 0,5 |
According to that matrix:
A. “B” would be a dominant strategy for firm 1
B. {“C”, “C”} (mutual investment in cost reduction) would be the Nash equilibrium of this game
C. None of the possible outcomes of this game is Pareto-optimal
D. There are three Nash equilibria in this game
E. None of the above
26. Which of these markets would be closest to a monopolistically competitive market?
A. The electricity market.
B. The market for mobile phone operators’ services in Russia.
C. The world market for cell phones.
D. The market for Treasury bonds (in absence of large players).
E. The Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange (MICEX).
The following three questions refer to this graph:
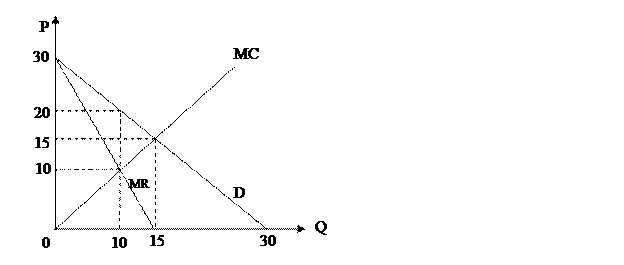
27. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total variable costs of this firm would equal:
A. 10
B. 100
C. 112,5
D. 50
E. 15
28. If this were a non-price-discriminating multi-plant monopoly, the deadweight loss from this market’s monopolization would equal:
A. 5
B. 50
C. 25
D. 75
E. 12,5
29. If this monopoly could perfectly price discriminate, the consumer surplus would equal:
A. 50
B. 100
C. 112,5
D. 225
E. 0
30. Consider a monopolized market in a state of equilibrium (Pm, Qm). The government introduces a price ceiling Pmax, Pmax < Pm. As a direct consequence of that…
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 167 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| D. both factors should bring the firm the same marginal product per dollar spent on them | | | Normal Profits and returns on investments |