
Читайте также:
|
Colonial Revival became a popular American house style after it appeared at the 1876 the US Centennial Exposition. Reflecting American patriotism and a desire for simplicity, the Colonial Revival house style remained popular until the mid-1950's. Between World War I and II, Colonial Revival was the most popular historic revival house style in the United States.
Some architectural historians say that Colonial Revival is a Victorian style; others believe that the Colonial Revival style marked the end of the Victorian period in architecture. The Colonial Revival style is based loosely on Federal and Georgian house styles, and a clear reaction against excessively elaborate Victorian Queen Anne architecture. Eventually, the simple, symmetrical Colonial Revival style became incorporated into the Foursquare and Bungalow house styles of the early 20th century.
Subtypes of the Colonial Revival House Style

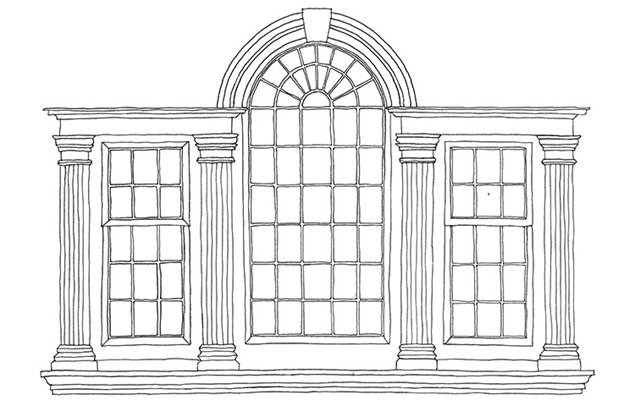
Palladian window
Also called a “Venetian window” or a “serliana”, this was an essential ingredient for most neoclassical buildings. A window in three parts, with the central light rising taller to be rounded off in an arch and the two side lights flanked by pilasters and crowned by entablatures. Smooth, smart and satisfyingly symmetrical.
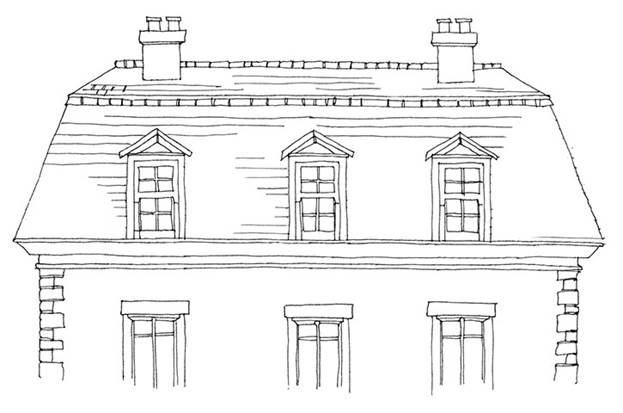
Mansard roof
An introduction of the late 18th century, this form of roof has four sloping sides, each of which becomes much steeper midway down. These were tall and spacious, and allowed owners of buildings to sneakily gain an extra floor without really looking like they’d done so. They were first popularised by French architect François Mansart in the baroque period and are also referred to as a French roof.
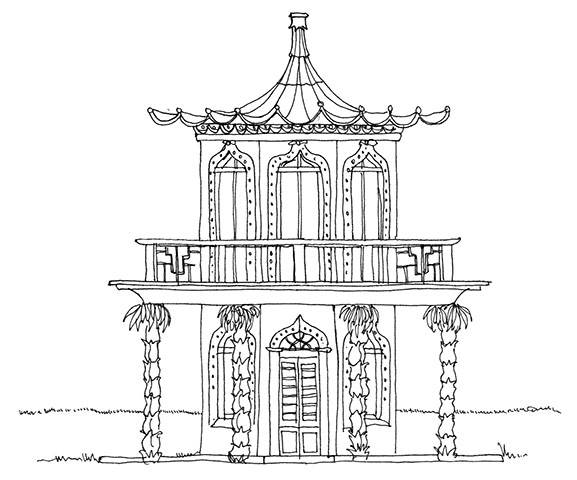
Chinoiserie
From the late 17th century, when China relaxed its foreign trade restrictions, Chinese fabrics and ceramics began to be seen in increasing quantities in the west. Soon every self-respecting household had a Chinese room, replete with decorative painted wallpapers, tiles, rugs and furnishings. The trend reached buildings some 50 years later in a filtered, exaggerated way, with results that bore little resemblance to anything you might actually see in China. Key characteristics included curling upturned eaves on roofs, lacquered or gilded mouldings, bas-reliefs and motifs such as dragons, birds, exotic flowers and figures in oriental dress.
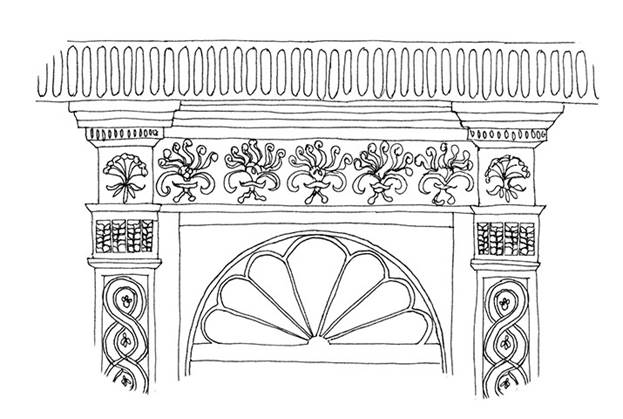
Stucco
This is the white render applied to late-Georgian facades that could also be sculpted and moulded for decorative purposes. It was a kind of weather-resistant plaster, traditionally made of lime and sand with the addition of fibres – plant or animal.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 178 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Colonial Revival House Styles | | | Сроки благоприятных фаз развития двигательных качеств 2 страница |