
Читайте также:
|
Control – manipulating some quantity to some desired value. It can be manual or automatic mechanism. (Ex. Cruise control, room temp. control by air cooler, disk control by the CD drive)
System – an object or collection of objects contains various components connected together that variation of one component affects the other components.
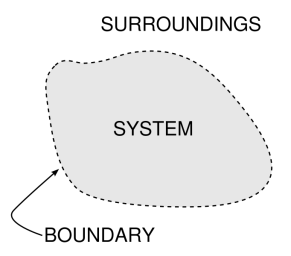 We scope a system by defining its boundary.
We scope a system by defining its boundary.
| Output |
| Input |
| System |
Static system – The output depends only on the current input, output does not change with the time if input is const.
Dynamic system – The output depends on current and earlier input, output changes with time even if input is const. It can be found in all major engineering areas (mechanical, electrical, thermal, fluid and mixed systems).
Ex. of control system: Robot CS (moves the robot arm with or without load, work in extreme environmental condition for appropriate actions according to existence.) Temp. CS (room temp. control, temp. control of an electric furnace, temp. control of a bus-compartment.)
Ex. Cruise control& Adaptive cruise control (-to move at a set of speed if there is no car in front,-to adjust range-clearance when preceding car brakes or accelerates).
Ex. Speed control of electrical motor (dc motor, induction motor, linear motor…)
Applications- power systems, manufacturing, robotics, process control, flight control and navigations, network control, biomedical, process scheduling)
Types of control:
Manual control -when person control a machine.
Automatic control – when a system is not controlled by human.
Regulator- the system always maintains steady output.
Tracking or Servo control - the system is used to track a reference output.
Open-loop control – if the controller doesn’t use the output to compute control signal.
Feedback(Close loop)Control –when the controller uses the output to compute the control signal.
Adaptive Control: uses real-time identification of the process parameters, or modification of controller gains, thereby obtaining strong robustness properties.
Optimal Control: minimizes a certain cost function.
Intelligent Control: use various AI computing approaches like neural networks, Bayesian probability, fuzzy logic, machine learning, evolutionary computation and genetic algorithms
Non-linear Control: deals with the control of non-linear systems.
| Control signal |
| Error |
| Output |
| Plant |
| Reference |
| Controller |

| Actuator |
| Process |
| Plant |
| Disturbance |
Controlled Variable -The quantity or condition that is measured and controlled. It is the Output of the Plant.
Manipulated Variable -The quantity that is varied by the controller to adjust the controlled variable or Output.
Plant -The physical object to be controlled. (Ex. a spacecraft, a reactor, heating furnace etc.). It is the combination of Process and Actuator.
Process -The operation of a plant to be controlled.
Actuator - The device that can influence the controlled variable of the process.
Disturbance - A signal that tends to adversely affect the output. It can be internal or external.
Systems -A combination of components that act together and perform a certain objective.
An open-loop control system utilizes an actuating device to control the process directly without using feedback.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Simple construction and easy of maintenance. | |
| Less expensive than a corresponding closed loop system. | Disturbance and changes in calibration causes error. |
| Convenient when output is hard to measure or not feasible. | Recalibration is necessary from time to time. |
A closed-loop control system uses a measurement of the output and feedback of the output signal to compare it with the desired output (reference or command).
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
PWM controllers switch the motor on and off in a series of pulses.
The voltage seen by the load is directly proportional to the source voltage

|
Duty Cycle: on-time / period
Vlow is often zero 
Analog PWM signals can be made by combining a saw- tooth waveform and a sinusoid.
| PWM output is formed by the intersection of the saw-tooth wave and sinusoid. |
 Applications to DC Motors
Applications to DC Motors
• The voltage supplied to a DC motor is proportional to the duty cycle
• Both brushed and brushless motors can be run with PWM
•
|
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 101 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Дописываем через запятую только OpenGL32.lib GLu32.lib | | | ГЛАВА 4, в которой молодой человек становится пленником |