
|
Читайте также: |
Consider a continuous time signal 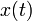 . Its one sided Laplace transform is defined as:
. Its one sided Laplace transform is defined as: 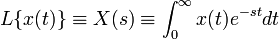
If the continuous time signal 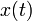 is uniformly sampled with a train of impulses to get a discrete time signal
is uniformly sampled with a train of impulses to get a discrete time signal 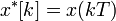 , then it can be represented as:
, then it can be represented as:
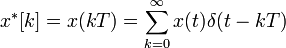
where 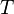 is the sampling interval.
is the sampling interval.
Now the Laplace transform of the sampled signal (discrete time) is called Star transform and is given by:
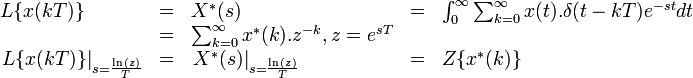
It can be seen that the Laplace transform of an impulse sampled signal is the star transform and is the same as the Z transform of the corresponding sequence when 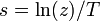 . Similar relationship holds when a continuous time system is converted into a sampled data system by cascading an actual impulse sampler at the input and a fictitious impulse sampler at the output.[7]
. Similar relationship holds when a continuous time system is converted into a sampled data system by cascading an actual impulse sampler at the input and a fictitious impulse sampler at the output.[7]
Дата добавления: 2015-08-27; просмотров: 76 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Relationship to Laplace transform | | | Relationship to Fourier transform |