
Читайте также:
|
Substances needed in the axon and dendrites are synthesized in the cell body and require transport to those sites.
Axonal transport may be described as:
-anterograde transport, which carries material from the perikaryon to the periphery
-retrograde transport, which carries material from the axon terminal and the dendrites to the perikaryon
The transport system may also be distinguished by the rate at which substances are transported:
-a slow transport system
-a fast transport s
Figure 34. Diagram of the different types of neurons; a, axon
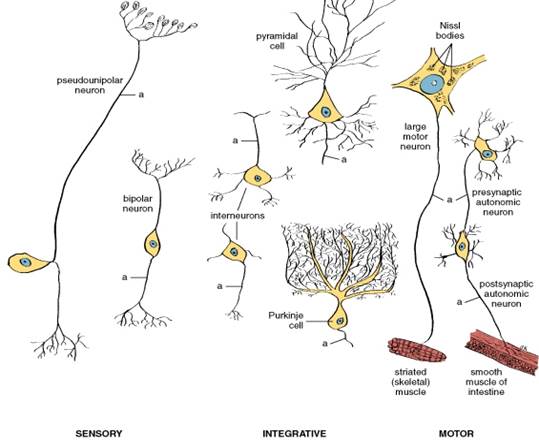
The neuron can be divided into three general categories:
-sensory neurons which convey impulses from receptors to the central nervous system (CNS)
-motor neurons which convey impulses from the CNS or from ganglia to effector cells
-interneurons or central neurons, form a communicating and integrating network between the sensory and motor neurons
 Neuroglia
Neuroglia
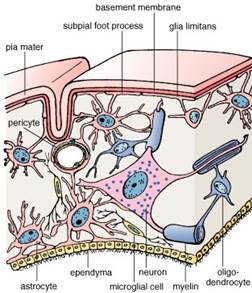
Figure 35. Distribution of glial cells in the brain
Within the CNS, the supporting cells are designated neuroglia or glial cells.
The neuroglia is divided into macroglia and microglia. The macroglia consists of next cell types:
1. Olygodendrocytes are irregular branching cells which are smaller that astrocytes with fewer and shorter processes. They are present in the white and gray matter of the CNS. Olygodendrocytes have next functions: formation of the myelin sheath in the CNS, insulators of the nerve fiber and supportive and nutritive function surrounding nerve cells.
Figure 36. Protoplasmic astrocytes in the gray matter of the brain (left), and fibrous astrocytes in the white matter of the brain (right)
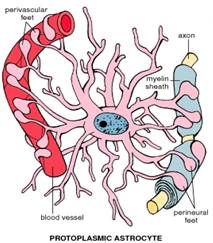
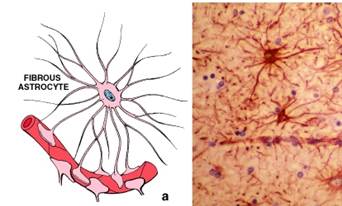
2. Astrocytes are star-shaped cells with long numerous processes. There are two types of astrocytes: fibrous (present in the white matter of the CNS) and protoplasmic (present in the gray matter of the CNS). Astrocytes have next functions: provide physical and metabolic support for the neurons of the CNS, and may share in the formation of the blood-brain barrier.
3. Ependimal cells are low columnar epithelial cells lining the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord. These cells produce cerebrospinal fluid by transport and secretion of materials derived from adjacent capillary loops.
4. Schwann cells have the same function as olygodendrocytes but are located around axons in the peripheral neuron system.
The microglia is originated from the blood monocytes. Microglia has small spindle-shaped cells. The branching processes arise from each pole of the cell. The cell body has spicules that project from their surfaces.
Function:
It is a phagocytic and immunological cell that plays a protective defense function in the CNS. They are called the police man of the CNS.
Дата добавления: 2015-07-25; просмотров: 137 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Synapses | | | Myelinated |