
Neurons communicate with other neurons and effector cells by means of synapses. Synapses are specialized junctions between neurons that facilitate transmission of impulses from one neuron to another.
Synapses between neurons may be classified morphologically as:
-axodendritic, occurring between axons and dendrites
-axosomatic, occurring between axons and the cell body
-axoaxonic, occurring between axons and axons
-dendrodendritic, occurring between dendrites and dendrites
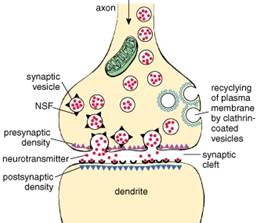 Figure33. Diagram of a chemical axodendritic synapse
Figure33. Diagram of a chemical axodendritic synapse
The synapse itself is formed three components.
1. Presynaptic membrane (component) is formed by an axon terminal, from which neurotransmitter is released.
2. Synaptic cleft is a thin intercellular space, that neurotransmitter must cross
3. Postsynaptic membrane (component) has receptor sites on the plasma membrane with which the neurotransmitter interacts.
The release of neurotransmitter by the presynaptic component can cause either excitation or inhibition at the postsynaptic membrane.
The most common transmitters are acetylcholine and norepinephrine.
Дата добавления: 2015-07-25; просмотров: 55 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Dendrites and axons | | | Axonal transport systems |