
Читайте также:
|
Macroeconomics
Division of economics concerned with the study of whole (aggregate) economies or systems, including such aspects as government income and expenditure, the balance of payments, fiscal policy, investment, inflation, and unemployment. It seeks to understand the influence of all relevant economic factors on each other and thus to quantify and predict aggregate national income.
Modern macroeconomics takes much of its inspiration from the work of Maynard Keynes, whose General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money 1936 proposed that governments could prevent financial crises and unemployment by adjusting demand through control of credit and currency. Keynesian macroeconomics thus analyses aggregate supply and demand and holds that markets do not continuously `clear´ (quickly attain equilibrium between supply and demand) and may require intervention if objectives such as full employment are thought desirable.
Development economics
The study of the history and changes in economic activity and organization over a period of time is called ` development economics´, and is one of the three major divisions of economic studies - the other two being macroeconomics and microeconomics. Development economics examines the attitudes and institutions supporting economic activity, as well as the process of development itself, and also includes the factors responsible for self- sustaining economic growth and the extent to which these factors can be manipulated by governmental policy.
Словарик:
Aggregate – прил. совокупный;
Competition – конкуренция (глагол compete - конкурировать);
Credit – зд. сущ. кредитование;
Economic activity – экономическая деятельность;
Expenditure – расходы;
Fiscal policy – финансовая (фискальная) политика.
Market price – рыночная цена;
Supply and demand – спрос и предложение (в т.ч. о законе);
Wages – зарплата (почасовая оплата в отличие от фиксированной salary).
4. Переведите на английский язык определение спроса, предложения и закона спроса и предложение. Данный русский нормативный текст является переводом с английского оригинала. Восстановление исходного языка значительно проще, чем перевод аутентичного оригинала.
Спрос: В экономике, количество товара или услуги, которые хотят купить потребители за любую цену. Кроме того, желание приобрести потребительский товар вместе со способностью заплатить за него.
Предложение: В экономике, производство товаров или услуг на рынок, поставляемых на рынок в преддверии ожидаемого спроса. Уровень спроса определяется ценой товара, его себестоимостью, уровнем технологий, доступных для производства, а также ценой других товаров. Нет никакой гарантии, что предложение будет соответствовать реальному спросу.
Спрос и предложение: Один из фундаментальных подходов в экономике, который рассматривает и сравнивает предложение товара со спросом на него (как правило, в виде графика кривых спроса и предложения, сплетающихся вокруг цены). Для типичного товара кривая предложения восходящая (чем выше цена, тем больше производитель готов продать), а кривая спроса нисходящая (чем дешевле товар, тем больше для него спрос). Точка, в которой пересекаются кривые, является равновесной ценой, при которой предложение равно спросу.
Словарик:
Восходящая/нисходящая кривая - upward-sloping/ downward-sloping curve
По любой цене – at any given price;
Потребительский товар – commodity;
Равновесная цена - equilibrium price
Реальный спрос – actual demand;
Себестоимость товара – cost of production;
Сплетаться (о линиях), наносить на чертеж – to plot.

On this picture, Vertical shows price of goods that tends to go down, Horizontal shows quantity of goods that tends to increase.
РАЗДЕЛ 2. ОСНОВНЫЕ СОСТАВЛЯЮЩИЕ РЫНОЧНОЙ ЭКОНОМИКИ
1. Прочитайте текст по материалам USIS (United States Information Service). Обратите внимание на выделенный текст: он содержит ключевые слова, определение которых потребуется на устном задании.
Every economic system tries to anticipate and then meet human needs through the production and distribution of goods and services. The economic system is the mechanism that brings together natural resources, the labor supply, technology, and the necessary entrepreneurial and managerial talents. Although the type of economic system used by a nation is the result of political decision, it is also in even larger part the result of a historical experience that, over time, becomes a national culture.
The first ingredient of an economic system is the natural resources from which goods are produced.
Second, the amount of available labor helps determine the health of an economy.
Another factor in any economic system is the quality of available labor -- how hard people are willing to work and how skilled they are.
But the existence of abundant natural resources and a skillful and willing labor force accounts for only part of the structure of an economic system. The resources must be directed as efficiently as possible into the areas where they will be most productive. In the American economy, managers of enterprises responding to signals from markets perform this function.
Large blocks of resources must be available for major investments. In America, entrepreneurs accumulate money and then invest in projects -- buy supplies, hire workers, produce and sell products -- that seem likely to give a high return on the original investment. This is determined on the basis of an assessment of the wants and needs of those who buy goods and services -- what is known as consumer demand.
In the United States, the corporation has proved to be an effective device for accumulating funds for investment. This is a voluntary association of owners, known as stockholders, who form a business enterprise that is marked by limited liability.
Generally there are three kinds of businesses: single-owner operated businesses, partnerships and corporations. The first two are important, but it is the latter structure that best permits the amassing of large sums of money by combining the investments of many people who, as stockholders, can buy or sell their shares of the business at any time on the open market. Corporations make large-scale enterprise possible.
Once the first entrepreneurial investment of capital has been made, someone must be hired to manage the new business, factory or other endeavor. Modern America has developed a chain of managerial command, from the foreman at the loading dock to the chief executive in the boardroom, whose job is to see that the business runs smoothly and efficiently. Good management often can make the difference between a successful or unsuccessful operation.
In the U.S. economic system, consumers, producers and the government make decisions on a daily basis, mainly through the price system. The dynamic interaction of these three groups makes the economy function. The market's primary force, however, is the interaction of producers and consumers; this has led analysts to dub the U.S. economic system a "market economy."
As a rule, consumers look for the best values for what they spend, while producers seek the best price and profit for what they have to sell.
Government, at the federal, state and local levels, seeks to promote the public safety, assure reasonable competition, and provide a range of services believed to be better performed by public rather than private enterprise. Some of these public services include the administration of justice, education (although there are many private schools and training centers), the postal (but not the telephone) service, the road system, social statistical reporting and, of course, national defense. Each level of government provides direct services. The postal system, for example, is a federal system serving the entire nation, as is the large military establishment. By contrast, the construction and maintenance of most highways is the responsibility of individual state governments. The public education systems are primarily paid for by state, county or city governments. In general, police and fire protection are the responsibilities of local government.
In this system, when economic forces are unfettered, supply and demand establish the prices of goods and services. Entrepreneurs are free to develop their businesses. In theory, unless they can provide goods or services of a quality and price to compete with others, they are driven from the market, so only the most efficient and those who best serve the public remain in business. In practice, government regulations can interfere with pure competition in order to promote other national policy objectives such as price and income stability, regional development or environmental preservation. Similarly, businesses can interfere with pure competition, through price fixing or other monopolistic practices, in order to maximize profits.
The government regulates and controls private enterprise in many ways in order to ensure that business serves the best interests of the people as a whole. Regulation is usually considered necessary in areas where private enterprise has been granted a monopoly, such as in electric or local telephone service, or in other areas where there is limited competition, as with the railroads. Public policy permits such companies to make reasonable profits, but limits their ability to raise prices "unfairly" (as defined by the regulators) because the public depends on their services. Often control is exercised to protect the public, for example, when the Food and Drug Administration bans harmful drugs, or requires standards of quality in food. In other industries, government sets guidelines to ensure fair competition without using direct control.
2. Словарик в порядке появления слова:
Anticipate – предвидеть;
Human needs – человеческие потребности;
Entrepreneur – предприниматель (прил. entrepreneurial);
Ingredient - составляющее, компонент;
Skills – навыки и умения (прич. skilled, прил. skillful);
Direct – управлять, направлять;
Productive – эффективный, продуктивный;
Block – массив;
Major investments – крупные инвестиции;
Accumulate money – собирать деньги, привлекать капитал;
Invest – вкладывать, инвестировать;
Consumer demand – потребительский спрос;
Corporation – зд. акционерная компания;
Funds – (финансовые) средства;
Association – зд. (добровольное) объединение;
Owner – владелец, собственник;
Stockholder, тоже что Shareholder – акционер, от share – акция;
Businesses – сущ. мн. компании, парная по числу форма к ед. business – компания, в отличие от только ед. business – дело, бизнес;
Agricultural /manufacture goods – сельскохозяйственные /промышленные товары;
Single-owner operated business = sole proprietorship – индивидуально-частное предприятие;
Partnership – зд. товарищество;
Business enterprise – деловое предприятие;
Chain of managerial command – система управления;
Chief executive (officer) – управляющий директор;
Boardroom, тоже что Board (of Directors) – правление;
Best value – лучший товар, лучшее применение деньгам;
Profit – прибыль;
Public services – общественные услуги, функции государственного сектора;
Direct services (of the government) = public services;
Government regulations – государственное регулирование;
Maintenance – обеспечение деятельности;
Price fixing – фиксирование цен;
Unfairly – несправедливо (ср. Fair game – честная игра)
Food and Drug Administration - Управление по контролю за продуктами и лекарствами (США) (это самый краткий из зафиксированных переводов);
Ban – запрещать.
2. Определите по-английски свое понимание следующих ключевых слов:
1) production and distribution of goods and services;
2) natural resources, the labor supply, technology, the entrepreneurial and managerial talents;
3) the quality of available labour;
4) the resources must be directed;
5) large blocks of resources vs. major investments;
6) consumer demand;
7) corporation as association of owners;
8) consumers look for the best values for what they spend, while producers…
9) supply and demand establish the prices of goods and services, unless…
10) government regulations can interfere with pure competition
11) public /direct services include…
12) Food and Drug Administration
3. Переведите на английский язык определение рыночной экономики из экономического словаря, изданного в России. Задача несколько облегчается тем, что в основе нормативного русского текста лежит английский первоисточник, поэтому при переводе вы не столкнетесь с семантическими лакунами или необходимостью серьезных синтаксических трансформаций:
РЫНОЧНАЯ ЭКОНОМИКА (market economy). Экономика, в которой значительная часть экономических решений принимается исходя из информации, предоставляемой рынками. Рыночную экономику следует отличать от плановой экономики, в которой большинство важных решений принимается в результате централизованного установления агрегатных количественных показателей. Преимущество рыночной экономики состоит в том, что формирующиеся на рынках цены передают информацию о спросе на различные товары и услуги и издержках их производства и поставки. Цены также создают стимулы к расширению прибыльных и сокращению неприбыльных видов деятельности. Недостатки чисто рыночной экономики состоят в том, что не учитываются внешние факторы (externalities), в том, что рынок может быть деформирован существованием монополий (monopolies), и в том, что итоговое распределение доходов может быть неприемлемым по социальным причинам. На практике в экономике большинства стран различным образом сочетаются элементы рыночного саморегулирования и государственного планирования.
Экономика. Толковый словарь. Общая редакция: д.э.н. Осадчая И.— М.: 2000. Источник: John Black. A Dictionary of Economics.
4. Вопросы для вынесения на обсуждение (требует дополнительной подготовки):
There are also other functions performed by the government when regulating the economy:
1) to control the extremes of boom and bust, and of inflation and depression, by adjusting tax rates, the money supply and the use of credit;
2) to control and, when necessary, to change the amount of public spending by the government itself with the aim to have a balanced federal budget;
3) to impose tariffs (duties) for imported goods or limit them by volume that permit certain products to remain relatively free from foreign competition,
4) to subsidy particular industries.
Can you comment to these functions or give as an example some other ones?
РАЗДЕЛ 3. СЕКТОРА ЭКОНОМИКИ И ОСНОВНЫЕ ТОВАРНЫЕ ГРУППЫ
1. Изучите одну из самых популярных моделей деления экономики на сектора:
| Primary Industries (excavating and harvesting) | Secondary Industries (processing and manufacturing) | Tertiary Industries (services) |
| agriculture, forestry, mining (minerals, incl. ores, fossil fuels, aggregates), fishing | petrochemical, metallurgy, machinery, electronics, building, pharmaceutical | banking, transportation, telecommunications, retail, healthcare, education |
Первая заголовочная строка колонки определяет сектора экономики.
Excavating – добыча полезных ископаемых;
Harvesting – сбор, промысел (относительно продуктов живой природы);
Processing – переработка;
Manufacturing – изготовление (о промышленных товарах);
Services – услуги, service industries – сфера услуг;
Вторая строка колонки дает примеры отдельных отраслей и товарных групп (product groups) данной отрасли:
Aggregates – щебень, песок и др.;
Agriculture – сельское хозяйство;
Fishing – рыбная промышленность;
Forestry – лесное хозяйство, лесная промышленность;
Fossil fuels – ископаемые виды топлива;
Minerals – полезные ископаемые;
Mining – горнодобывающая промышленность, разработка месторождений;
Ore – руда.
Building, Construction – строительство;
Electronics industry – электронная промышленность;
Machinery – машиностроение;
Petrochemical industry – нефтехимическая, нефтегазохимическая отрасль.
Retail – розничная торговля;
Banking – банковская отрасль;
Education – сфера образования;
Healthcare – здравоохранение;
Retail – сфера розничных услуг;
Telecommunications – транспортная отрасль;
Transportation – сфера транспорта.
2. Задание: Какие еще отрасли вы знаете? Дополните этот список.
3. Прочитайте статью с разъяснениями к таблице, перескажите ее, используя таблицу (1):
3 Sector Models of Economics (from eHow at http://www.ehow.com)
The Three Sector Hypothesis of economics was based largely on the work of A. G. B. Fisher in 1933 and Colin Clark in 1940. The Fisher-Clark model of economics provides a description of the types of activities important in all societies. Fisher and Clark also described how the economy changes over time, and how this changes the activities of the society.
Primary Sector
The primary sector in an economy refers to the production or harvesting of natural resources. Activities of the primary sector include agriculture, fishery, mining, and forestry. The primary sector involves the use of physical space or the withdrawal of materials from physical space.
Secondary Sector
The secondary sector of an economy is the manufacturing sector. In this stage of production, natural resources are processed or refined for further use. Construction, baking, assembly, and other industries are part of the secondary sector, which uses products from the primary sector to create consumer goods.
Tertiary Sector
The tertiary sector involves services provided related to the other two sectors. Retail, banking, and sales are all part of the services sector. This sector doesn't involve production, but rather the support of production that occurs in the first and second sectors.
Quaternary and Quinary Sectors
Later theorists, such as Paul Hatt and Nelson Foote, included quaternary and quinary sectors to the economic model. These theorists felt the service or tertiary sector was overly large and should be divided up. The quaternary sector refers to intellectual- or information-related positions, so its activities include healthcare, education, government, and information technology. The quinary sector refers to top-level executives in any part of the service sector, including CEOs, high-level government officials, and education and healthcare administrators.
Fisher-Clark Hypothesis
Fisher and Clark stated that workers in pre-industrialized societies were predominantly involved in the primary sector, particularly in agriculture. As industrialization occurs in a society, employment becomes concentrated in the manufacturing or secondary sector. In a post-industrial society, manufacturing becomes less important, and the service sector or tertiary sector gains prominence.
2. Комментарии.
1) В зарубежной экономической науке под сектором экономики также понимается совокупность институциональных единиц, имеющих сходные экономические цели, функции и поведение. Соответственно этому подходу все субъекты экономики группируются в четыре сектора: сектор домашних хозяйств; сектор предприятий (финансовых и нефинансовых); сектор государственных учреждений; внешний сектор. К модели отраслевого деления данного раздела такая классификации прямого отношения не имеет.
2) В советской экономике присутствовало деление отраслей на принадлежность к группе «А», группе «Б», к сфере нематериального производства. С этого времени в названии самих отраслей по профилю деятельности мало что изменилось, но язык классификаций изменился. В нашем исключительно языковом пособии мы в данной связи предостерегаем от вольного (как встречается) калькирования английской терминологии (например, если русский термин «первичный сектор» вполне уместен, т.е. как «базовый» сектор, то «вторичный сектор», «третичный» и т.д. вряд ли соответствуют традициям и нормам русского языка экономики).
3) Распределяя отрасли по секторам, можно заметить по житейскому опыту, что граница между ними весьма прозрачна. Нынешние крупные компании занимаются добычей сырья, они же занимаются его переработкой, а также торговлей и даже доведением конечного продукта до потребителя (вспомните бензоколонки «Лукойл»). Поэтому в составе промышленности функционируют такие межотраслевые комплексы, как топливно-энергетический, металлургический, машиностроительный и др. Более сложной структурой отличаются строительный и агропромышленный комплексы, объединяющие разные отрасли национальной экономики. Тем не менее, классификация оперирует очевидными категориями, и хотя она создана в связи с вопросами экономической теории, а не вопросами перевода, переводчик может ей успешно воспользоваться для лучшего оперирования тематическими группами лексики.
4. Прочитайте небольшую подборку материалов об экономике Великобритании, она содержит ряд слов, относящихся к отраслевому производству (дополните ими список (1), а также экономические термины (их перевод в конце параграфа).
Economy in Britain
The UK is the sixth-largest economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP) and eighth-largest measured by purchasing power parity (PPP). It has the third largest economy in Europe, after Germany and France (measured by both nominal GDP and PPP in both cases). The UK's GDP per capita is the 22nd highest in the world in nominal terms and the 22nd highest measured by PPP. The British economy encompasses the economies of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland (in descending order of size). The UK has one of the world's most globalised economies. The capital, London, is one of the two largest financial centres in the world, along with New York City, and has the largest city GDP in Europe. To large extent this is due to one of the world’ largest stock of both inward and outward foreign direct investment (the third-largest after the United States and France). The UK economy is considered as one of the strongest in Europe also because inflation, interest rates, and unemployment remain low. The UK is currently ranked seventh in the world in the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business index.
Currency of Great Britain in Pound Sterling (£) = 100 pence (p)
Britain’s main industries today are banking and finance, steel, transport equipment, oil and gas, and tourism. Other industries include: machine tools, electric power equipment, automation equipment, railroad equipment, shipbuilding, aircraft, motor vehicles and parts, electronics and communications equipment, metals, chemicals, coal, petroleum, paper and paper products, food processing, textiles, clothing, and other consumer goods.
The pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures (after the United States and Japan).UK pharmaceutical companies make three of the world's best selling medicines: 'Zantac' (made by Glaxo Wellcome) for ulcer treatment; 'Tenormin' (ICI), a beta-blocker for high blood pressure; and 'AZT' (Glaxo Wellcome), a drug used in the treatment of AIDs.
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanized, and efficient by European standards, producing about 60% of food needs with only 1.4 % of the labour force. Its produce includes cereals, oilseed, potatoes, vegetables, cattle, sheep, poultry, fish. Around two thirds of production is devoted to livestock, one third to arable crops. The lowlands support some farming such as wheat, potatoes and vegetables. Dairy and sheep farming are common in the hilly pastures.
Energy. The UK has large coal, natural gas, and oil reserves; primary energy production accounts for 10% of GDP, one of the highest shares of any industrial nation. The British economy is boosted by North Sea oil and gas reserves, valued at an estimated £250 billion in 2007. British Petroleum (BP) is Britain's biggest industrial company.
Services. Services, particularly banking, insurance, and business services, account by far for the largest proportion of GDP. Britain is responsible for 10 per cent of the world's export of services, including banking, insurance, stockbroking, consultancy and computer programming.
Exports of goods and services made in 2006 $468.8 billion f.o.b. Exported products included manufactured goods, fuels, chemicals; food, beverages, tobacco. The chemical industry is Britain's largest export earner. Britain is also a major supplier of machinery, vehicles, aerospace products, electrical and electronic equipment. The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry, depending upon the method of measurement.
Для справки:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) – валовый национальный продукт (ВВП);
GDP per capita – ВВП на душу населения.
Краткое определение:: GDP is the market value of all final goods and services produced and purchased within a country during a given time period.)
In 2006 UK’s GDP was estimated as US $1.93 trillion. It’s composition by sector was: agriculture: 1%, industry: 25,6%, services: 73.4%.
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) - паритет покупательной способности.
Краткое определение: PPP is a rate of exchange between two currencies that gives them equal purchasing powers in their own economies is an economic theory that states residents of one country should be able to buy the goods and services at the same price as residents of any other country over time.
Globalised economy. Слово «глобальный» имеет длительную историю существования в русском языке, поэтому его новое употребление в отношении мирового экономического пространства под воздействием понятия global economy разумно и удобно. Однако под влиянием часто встречающихся английских форм globalized и globalizing в русской среде тоже стали появляться формы «глобализированный» и даже «глобализирующий». Переводчику следует с осторожностью относиться к таким словоупотреблениям, поскольку это все же причастные формы от глагола «глобализировать», который в чисто экономическом смысле пока ограничен в употреблении. Ср. глобализировать проблему, но * глобализировать компанию. Если взять статью англо-русского словаря: «globalize эк. глобализировать, глобализироваться (распространять какую-л. деятельность или влияние за пределы отдельной страны, напр., выводить предприятие на мировой рынок), to globalize a company — глобализировать компанию» то такой перевод относится к категории семантических варваризмов, когда используется интернационализм латинского происхождения, но не имеющий в языке перевода данной семы. Если приводимая словарем иллюстрация Most African companies are seeking to globalize соответствует узусу употребления в английском языке, то предлагаемый перевод «Почти все африканские компании стремятся глобализироваться» нормативным считать нельзя. Тем более что в русском языке существуют возможности компактно передавать этот смысл, используя глаголы интегрировать, интегрироваться, распространиться, выйти на уровень и др.
Словарик далее по ходу появления слов:
Stock – акции в целом;
Inward foreign investment – иностранные капиталовложения внутри страны;
Outward foreign investment – капиталовложения за рубежом;
Interest rate – банковская процентная ставка;
World Bank's Ease of Doing Business index – индекс легкости ведения бизнеса, присваиваемый Всемирным банком;
Pound Sterling – британская валюта фунт стерлингов, также известная как British pound – фунт;
Produce – зд. сущ. продукция(только сельскохозяйственная);
Share – зд. доля (на рынке);
Value – гл. оценивать;
Estimate – оценивать;
Banking – банковские услуги, банковские операции;
Insurance – страхование;
Stockbroking – фондовые операции;
f.o.b. = free on board – коммерческий термин базисных условий поставки = ФОБ (ответственность продавца заканчивается погрузкой на судно покупателя); в русских коммерческих документах присутствует как f.o.b. или транслитерация ФОБ, используемые ранее русские эквиваленты базисных условий со словом франко- из обихода вышли.
Earner – сущ. от гл. earn – зарабатывать;
Market value – рыночная стоимость.
5. Разберемся с присутствующим в тексте менее знакомом понятием – «паритет покупательной способности» – Purchasing Power Parity.
5.1. Прочитайте выдержку из учебного пособия, размещенного (http://knigi-uchebniki.com/ekonomika-mejdunarodnaya/103-teoriya-pariteta-pokupatelnoy.html)
«Самым простым подходом к пониманию этого взаимодействия является сравнение цен одного и того же товара, продаваемого в разных странах. Это сравнение получило название «закон единой цены», согласно которому в условиях совершенной конкуренции при отсутствии транспортных издержек и торговых барьеров, одинаковые товары должны продаваться в разных странах по одинаковой цене, если ее выразить в одной и той же валюте. Если, например, курс рубля к евро составляет 30 руб. за 1 евро, то шерстяной свитер, продаваемый в Мадриде за 100 евро, должен продаваться в Москве за 3000 руб., что равнозначно 100 евро при курсе 30 руб. за 1 евро. <…> Но сравнение цен одного товара не является репрезентативным для получения представления о ценовой ситуации в стране в целом. В 1916 г. шведским ученым Густавом Касселем была предложена теория, предусматривающая возможность определения обменного курса на базе общего уровня цен в стране. Она получила название «паритет покупательной способности» (ППС). Согласно этой теории обменный курс между валютами двух стран равен соотношению уровней цен в этих странах. За основу уровня цен страны принимается цена не одного товара, а представительного набора наиболее покупаемых потребительских товаров. Этот набор обычно именуют потребительской корзиной. <…> Приведенный пример указывает на тесную взаимосвязь внутренней покупательной способности валюты страны с ее курсом. Если покупательная способность национальной денежной единицы на внутреннем рынке падает (растет уровень цен), это будет означать ее пропорциональное обесценение на международном валютном рынке.
5.2. Теперь сравним прочитанное с разъяснением, данным InvestorWords.com на термин Purchasing Power Parity:
The theory that, in the long run, identical products and services in different countries should cost the same in different countries. This is based on the belief that exchange rates will adjust to eliminate the arbitrage opportunity of buying a product or service in one country and selling it in another. For example, consider a laptop computer that costs 1,500 Euros in Germany and an exchange rate of 2 Euros to 1 U.S. Dollar. If the same laptop cost 1,000 dollars in the United States, U.S. consumers would buy the laptop in Germany. If done on a large scale, the influx of U.S. dollars would drive up the price of the Euro, until it equalized at 1.5 Euros to 1 U.S. Dollar - the same ratio of the price of the laptop in Germany to the price of the laptop in the U.S. The theory only applies to tradable goods, not to immobile goods or local services. The theory also discounts several real world factors, such as transportation costs, tariffs and transaction costs. It also assumes there are competitive markets for the goods and services in both countries.
Узнавая в английском отрывке элементы содержания прочитанного выше русского отрывка, передайте своими словами его общий смысл.
6. Расскажите по-английски, какими отраслями экономики представлен на карте России ваш родной город, область, край.
РАЗДЕЛ 4. ПРОФИЛЬ И СТРУКТУРА КОМПАНИИ
1. Profile of the company - «Профиль (карта) компании».
Это основная информация о компании. Она базируется на уставных документах, истории и текущей практической деятельности компании. Содержится в базах данных регистрационных, налоговых и других официальных органов. Предоставляется компанией по личному запросу своих потенциальных партнеров в порядке установления деловых отношений. Основные данные по профилю компании находятся в свободном доступе у торгово-промышленных палат страны регистрации. В том или ином виде отражается в рекламных продуктах компании.
| Name of the Company | Название компании (включает аббревиатуру статуса или не включает при наличии бренда) | |
| Status, synonym: Form of ownership | Статус, Организационно-правовая форма (уточняется в том числе при наличии аббревиатуры в названии) | |
| Occupation (is occupied with / deals with), synonyms: Product area, Activities | Сфера деятельности | |
| Period of Operation (the company was established in/ the business first started/ the company has been in business since) | Год учреждения компании | |
| Location (located / based) incl. Main headquarters, | Национальная принадлежность – определяется по указанию размещения головного офиса | |
| Number of personnel | Количество работающих | |
| Divisions in other countries | Подразделения в других странах | |
| Names of head persons (chairperson of the board, managing director / CEO) | Имена руководителей (председатель правления, управляющий директор) | |
| Last year revenues / total sales volume | Выручка /оборот за прошлый год (обязательно в открытом доступе для открытых акционерных компаний |
Дополнительно могут указываться сведения о принадлежности компании деловым объединениям (вхождение в состав холдинга, концерна, группы компаний и др.), также указываются крупные мажоритарные акционеры или ее абсолютные собственники.
2. Примеры размещения основных сведений о компании.
2.1. Ознакомимся со сведениями о компании ABB в четырех вариантах.
2.1.1.
Type Publicly traded limited company
Traded as SIX: ABBN, NYSE: ABB, OMX: ABB, NSE: ABB, BSE: 500002
Industry Electrical equipment
Founded 1988 through merger of ASEA (1883) of Sweden and Brown, Boveri & Cie (1891) of Switzerland
Headquarters Zürich, Switzerland
Area served Worldwide
Key people Joe Hogan (CEO), Hubertus von Grünberg (Chairman)
Products Power technology, Industrial automation
Revenue US $39.337 billion (2012)
Operating income US $3.838 billion (2012)
Profit US $2.704 billion (2012)
Total assets US $28.002 billion (2012)
Total equity US $16.906 billion (2012)
Publicly traded limited company – открытое акционерное общество;
Traded as – акции торгуются на фондовых биржах; в биржевых списках компания фигурирует под кодом (сокращением или номером), далее представлены официальные сокращения называний мировых бирж: SIX – Swiss Exchange, NYSE – New York Stock Exchange, OMX – Helsinki Stock Exchange, NSE – National Stock Exchange of India, BSE – Bombay Stock Exchange;
Operating income – операционный доход (непосредственно от производства);
Total assets – общая сумма активов;
Total equity – общая сумма собственного капитала.
2.1.2.
ABB is a multinational corporation headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland, operating in robotics and mainly in the power and automation technology areas. It is ranked 143rd in the Forbes Ranking (2010).
ABB is one of the largest engineering companies as well as one of the largest conglomerates in the world. ABB has operations in around 100 countries, with approximately 145,000 employees in June 2012, and reported global revenue of $40 billion for 2011.
ABB is traded on the SIX Swiss Exchange in Zürich and the Stockholm Stock Exchange in Sweden since 1999, the New York Stock Exchange in the United States since 2001, September 2005 on London Stock Exchange and in November 2005 on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange.
2.1.3. Who we are - ABB in brief
ABB is a global leader in power and automation technologies. Based in Zurich, Switzerland, the company employs 145,000 people and operates in approximately 100 countries. The firm’s shares are traded on the stock exchanges of Zurich, Stockholm and New York.
ABB’s business is comprised of five divisions that are in turn organized in relation to the customers and industries we serve.
The company in its current form was created in 1988, but its history spans over 120 years. ABB’s success has been driven particularly by a strong focus on research and development. The company maintains seven corporate research centers around the world and has continued to invest in R&D through all market conditions.
The result has been a long track record of innovation. Many of the technologies that underlie our modern society, from high-voltage DC power transmission to a revolutionary approach to ship propulsion, were developed or commercialized by ABB. Today, ABB stands as the largest supplier of industrial motors and drives, the largest provider of generators to the wind industry, and the largest supplier of power grids worldwide.
Справка:
Research and Development (R&D) – исследования и разработки, аналог русскому термину НИОКР – научно-исследовательские и опытно- конструкторские разработки;
Maintain – поддерживать работу;
Commercialize – выводить на рынок;
Supplier – поставщик. Обратите внимание:
Словообразовательное гнездо (to) supply гл., supply сущ., supplier присутствует в экономических текстах в разных значениях и употребления. Ранее мы встретили supply «спрос» как термин экономической теории; supplier во фразе individuals are considered as suppliers of labour звучит метафорично и тоже понимается в плане теории, то есть в том смысле, что люди представляют собой трудовой ресурс и предоставляют труд как товар. В данном разделе мы подошли к самой употребительной, основной сфере употребления этих слов, обозначающих краеугольные понятия реальной экономической жизни: supply «поставлять (товар)», supply «партия товара», supplier «поставщик (товара)». Это в том числе коммерческие термины, являющиеся элементом контрактной лексики.
Приведенный в параграфе текст взят из актуального сайта компании www.abb.com. Сравните в деталях содержание этого теста с аналогичной справкой двадцатилетней давности (в тексте упомянута валюта ЭКЮ – «европейская валютная единица», которая использовалась как предшественник евро с 1979 по 1998 год).
2.1.4. ABB (electrical engineering)
[206,000 employees. 1300 companies. Over 500 profit centres. 11 JV in China]
We’re a multinational company with a quarter of a million employees and there are over a hundred and twenty subsidiaries worldwide. The group has a turnover of thirty one thousand, six hundred and twenty six million ECUs and our holding or parent company is located in the Netherlands.
About half our sales are to the professional and industrial markets. Altogether we manufacture and sell over a million different electrical products.
The group is also working in joint ventures with other partners. For example, we’re expanding our activities in China at the moment, developing business ventures with the People’s Republic.
Словарик:
Holding company = Parent company – головная компания холдинга, материнская компания;
Subsidiary – дочерняя компания;
Joint venture (JV) – совместное предприятие.
2.1.5. Вопросы для обсуждения:
- what is the difference in the format of these descriptions?
- what information is common for all four descriptions?
- what changes in activities or focuses on activities occur from report to report?
2.2. Проанализируйте информацию о ныне действующей тайской компании (2.2.1) с информацией о ней на уже несуществующем сайте (2.2.2). Словарик и комментарии к новым терминам даны в (2.2.3).
2.2.1. Company Profile
Basic Information
Company Name: Pechsiam Group Co.,Ltd.
Business Type: Manufacturer
Main Products: Long Grain, White Rice, White Rice Brokens
Number of Employees: 11 - 50 People
Trade & Market
Main Markets: Southeast Asia
Total Annual Sales Volume: US$2.5 Million - US$5 Million
Export Percentage: 91% - 100%
Factory Information
Factory Location: Nakhonpathom Province, THAILAND
Number of Production Lines: Above 10
Number of R&D Staff: Less than 5 People
Number of QC Staff: Less than 5 People
Contract Manufacturing: OEM Service Offered Buyer Label Offered
http://www.alibaba.com/product/th101922863-215637851-0/THAI_FRAGRANT_PERFUME_LONG_GRAIN_WHITE_RICE.html
2.2.2. Pechsiam Manufacturer and Exporter
1999 'WWW.PECHSIAM.COM' Established as Globalization B2B
2001 'Khun Tan' Brand of Thai Rice Export to the World Market.
2002 Natural Rubber NRL, RSS, ADS, LATEX started export B2B
2003 Canned Fruit and Vegetable started export B2B
2004 Sweetened Condensed Milk started export B2B
2005 Established as "Pechsiam Group"
2006 Expanded into MICE (meeting-incentive-conference-exhibition)
Company Profile
We are a joint-venture enterprise the utilized Asian Countries in manufacturing, exporting, marketing and distribution company operating in the food and other fast moving consumer goods categories.
The whole production process is in strict conformity with international standards, and constant research and development all products. We are confident that our products and services will satisfy the highest of standards.
Since its founding in 1999, we remained committed to realize "A more nurturing environment for humanity and Earth"
We continue to develop industry-leading products by maintaining our "Customer-first, Quality-first" policy, thus consolidating the total power and ability of Global Pechsiam.
Как вы заметили, материал (2.2.2) страдает серьезными погрешностями в английском языке. Это всегда отталкивает потенциальных клиентов и партнеров, и сейчас никакая компания не может себе этого позволить, будь то азиатская или российская. Тем не менее, материал отвечает ряду требований «профиля», видимо, и поэтому тоже компания удержалась на рынке.
Задание: Отметьте успешные моменты информации и, по возможности, отредактируйте язык.
Словарик терминов с пояснениями:
QC Staff = Quality Control Staff – штат по контролю за качеством продукции.
OEM = Original Equipment Manufacturer – обозначает производство компонентов, которые приобретаются фирмой-покупателем и далее продаются потребителю или используется в изделии под именем бренда покупателя;
OEM Service Offered – производитель предлагает взять на себя дальнейший ремонт и обслуживание поставляемого товара;
Buyer Label Offered – производитель предлагает наносить этикетку с именем покупателя при изготовлении своей продукции.
Еще по поводу OEM: этот термин особо популярен на автомобильном рынке (automotive market). Подразумевается, что при необходимости замены агрегата и даже расходных материалов автомобиля желательно произвести замену именно «родным» компонентом. Так, для автомобилей BMW радиаторы поставляет только Behr, а свечи зажигания поставляют три производителя — Bosch, NGK и Beru, но только эти три. Таких узлов и материалов у автомобиля около 50, и все вместе они обеспечивают качество одного из самых престижных брендов. Это не означает, что нельзя подобрать замену узла товаром другого производителя. Но это не будет OEM, а без OEM это уже будет не совсем BMW. Аналогичный подход присутствует сейчас и на других товарных рынках. И это обусловлено целым рядом факторов, среди которых лояльность, престиж и просто вопросы качества. В русских текстах термин воспроизводится на латинице.
B2B = Business to Business — сектор рынка, ориентированный на организацию взаимодействия между компаниями в процессе производства и продажи товаров или услуг; является узкоспециальным термином и воспроизводится в латинице.
MICE – аббревиатура-акроним [mais], буквы обозначают четыре ключевые составляющие делового туризма: M – Meetings (встречи), I – Incentives (поощрение, стимулы), С – Conferences / Conventions (конгрессы, конференции), E – Exhibitions / Events (выставки, мероприятия, события). Есть шутка, что ЦРУ понимает под буквами процедуру вербовки: Money, Ideology, Compromising, Egotism (деньги, идеология, компромат, самомнение). Термин, как и в случае выше, воспроизводится на латинице.
Production process – производственный процесс.
Обращаем внимание, что англ. production обозначает именно производство, а не продукцию, как может показаться, особенно при переводе с русского на английский. Продукция – это product, produce (о сельхозпродукции), output. Есть исключения, когда production обозначает театральную постановку или выборную кампанию.
In strict conformity with … – в строгом соответствии c…
Синонимы: …in compliance with…
…following the requirements of…
…conforming the requirements of…
…as to…
Без этих выражения не обходится техническая документация, в том числе ссылающаяся на нее контрактная документация. В международной торговле фигурируют такие национальные технические стандарты, как российский ГОСТ (GOST), немецкий DIN, британский BSI, американский ASTM. В современном мире действует большое число обязывающих стандартов, они разрабатываются применительно к разным сферам человеческой деятельности и имеют характер международных предписаний. В практику российских компаний, причем не обязательно связанных непосредственно с международной деятельностью, широко внедрился международный стандарт ISO (the International Ogranization for Standartization). Компании проходят сертификацию на соответствие таким стандартам, как ISO 9000 Quality management (Управление качеством), ISO 14000 Environmental management (Экологический менеджмент), ISO 26000 Social responsibility (Социальная ответственность). Облегчает общение знание стандартов ISO 3166 Country codes (Коды стран), ISO 4217 Currency codes (Коды валют), ISO 639 Language codes (Коды языков).
3. Задание:
1) Подготовьте презентацию о компании, которой гордится ваш город, область.
2) Подготовьте презентацию об иностранной компании с международно известным брендом. Обратите внимание на то, входит ли эта компания в более крупные объединения или, наоборот, она владеет компаниями, имеющими собственный бренд.
4. Организационная структура компании.
The structure of the company depends on its specific economic targets and size. However, many aspects of the activity are common to all companies irrespective of their size and whether special departments and units are responsible for that, or these functions are delegated to the person in charge.
4.1. Направления деятельности.
Выбранная последовательность подбора названий отделов в какой-то степени отражает потребность предприятия в выделения их функций в особую структурную единицу по мере роста и возрастания нагрузки на те или иные направления деятельности. Этот список открытый.
| Department | Отдел | |||
| Production | Производство | |||
| Research and Development (R&D) | Исследования и разработки (НИОКР) | |||
| Marketing | Sales | Сбыт | Продажи | |
| Market Research | Маркетинг (1)* | |||
| Finance | Accounting and Control | Финансы | Бухгалтерия (расчетный отдел) | |
| Planning | Планирование | |||
| Purchasing and Logistics | Материально-техническое снабжение | |||
| Information Technologies (IT) | Информационные технологии (ИТ) | |||
| Public Relations | Communications | PR (2)* | Общественные связи | |
| Advertising | Реклама | |||
| Legal Affairs | Юридический | |||
| Personnel or Human Resourses | Персонала или кадров | |||
(1)* Мы придерживаемся взглядов тех российских экономистов, которые объем понятия «маркетинг» соотносят с английским market research (marketing research). Ср. в английском:
Marketing – The process by which products and services are introduced to the marketplace;
Market research – The collection and analysis of information about consumers, market niches, and the effectiveness of marketing programs (www.investorwords.com)
Соответственно, маркетинг как деятельность представляет собой комплекс действий предприятия по сбыту товара в фазе ее осмысления, она основана на предвидении и удовлетворении спроса потребителя и других компонентов анализа, таких как конкурентная ситуация и маркетинг-микс (marketing mix). В этой связи из двух допустимых вариантов ударения в заимствовании – на первый слог (как в языке-доноре) и на второй – мы выбираем марк е тинг. Вместе с тем мы наблюдаем такой подход к значению термина в русском языке, который соотносит понятие с английским marketing. В таком понимании маркетинг – это комплексная система организации производства и сбыта товаров или оказания услуг, основанная на предвидении и удовлетворении спроса потребителя, это совокупность процессов создания, продвижения и предоставления ценностей покупателям и управления взаимоотношениями с ними с выгодой для организации. Можно заметить, что в таком понимании маркетинг поглощает не только некоторые функции непосредственно сбыта, но также PR и рекламы.
2)* Понятие PR (пиар, общественные связи) также пока не устоялось в русском языке в практике применения. Российская экономика восприняла понятие Public Relations в первую очередь по его ясной внутренней форме, и без труда появилась калька «общественные связи». Звучание термина располагает к его пониманию как созданию положительного имиджа лица, компании, товара и пр., чем, собственно, и ограничивается деятельность российских PR-фирм и отелов предприятий. Тогда как в США уже к началу 1930-х годов PR сложились как самостоятельная функция менеджмента. Сейчас на западе PR-консалтинг включает лоббизм, поддержки продаж, более того, отношения в финансовой сфере и даже так называемый проблемный менеджмент, связанный с управлением в кризисных ситуациях.
Переведите следующие краткие определения PR из разных источников:
1) “PR - Efforts to establish and maintain a company's image with the public”.
2) “Public relations (PR) is the practice of managing the flow of information between an individual or an organization and the public”.
3) “Public relations is a strategic communication process that builds mutually beneficial relationships between organizations and their publics.”
В рамках нашего лингвистического практикума мы ставим целью определить специфику терминов с пересекающимся объемом понятий и правильно позиционировать тексты в процессе перевода, а это бывает не простой задачей, поскольку перевод в окончательном виде должен соответствовать оригиналу и одновременно удовлетворять ожиданиям реципиента, которому адресован перевод, а эти ожидания могут находиться в иной плоскости.
 Задание: проанализируйте элемент организационной схемы отдельного российского предприятия и переведите ее.
Задание: проанализируйте элемент организационной схемы отдельного российского предприятия и переведите ее.
Взяв за основу такое понимание маркетинга, измените таблицу в начале подраздела.
4.2. Структура управления.
Структура управления зависит от величины компании и формы собственности. Но принципиально управление выглядит так:
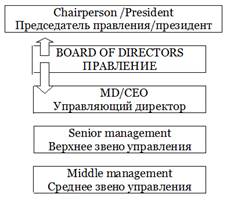 Задание: Переведите на английский:
Задание: Переведите на английский:
Вершиной иерархии компании является Правление, избираемое акционерами, которое возглавляет Председатель или Президент. Правление отвечает за решения и стратегию компании. Обычно оно назначает Управляющего директора, который несет общую ответственность за ведение дел.
Верхнее управленческое звено возглавляет отделы, такие как производственный, НИОКР, финансовый, общественных связей и др.
Комментарии:
1) Использование слова «директор» относится к британской традиции. Функционально русскому «генеральному директору» соответствует Managing Director (MD), также соответственно Financial Director, Commercial Director и т.д. Американским соответствием является Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Chief Financial Officer (CFO), Chief Commercial Officer (CEO) и т.д. Распространенной ошибкой при переводе является перевод CEO как «исполнительный директор» (в соответствии со словом executive). Это неверно с точки зрения правила соблюдения тождественности функций: в русском языке «исполнительный директор» подчинен «генеральному директору». Лучший вариант перевода – так же, как и британского наименования должности – «управляющий директор». Так же неверно переводить русское наименование «генеральный директор» как General Director, поскольку такое словосочетание в языке перевода не присутствует. Сочетание director general (по аналогии с secretary general) также не используется. Лучший вариант перевода – managing director. Примечательно, что последние годы директора российских предприятий предпочитают подавать себя не как прежде «генеральные», а именно как «управляющие директора», что облегчает жизнь переводчиков при осуществлении международных контактов.
2) Английскому Board of Directors (иногда этот орган называют Boardroom) традиционно соответствует русское «Правление». Последние десятилетия в русском обиходе устоялась калька «совет директоров». Устоялась настолько, что новички в экономике даже подозревают разницу в функциях этих, как им кажется, разных органов. Это абсолютные синонимы! Переводчику при обеспечении международных контактов следует придерживаться того варианта наименования, который зафиксирован в уставных документах российского предприятия.
3) Акционеры на ежегодном собрании избирают правление, правление избирает председателя правления (Chairman, Chairperson of the Board / President) и назначает / нанимает управляющего директора. Иногда функции управляющего директора может взять на себя председатель правления.
4) В английском есть ряд синонимов с значением «управлять структурой», разделим их на три группы по оттенкам в употреблении:
– to head, to manage, to administer, to run, to have overall responsibility;
– to be in charge of, to be responsible for (наиболее нейтральные для любого уровня ответственности;
– to command (наиболее жеcткий оттенок, по образцу военного подчинения), to control (управлять и контролировать), to supervise (осуществлять общий контроль, заведовать, но также и надзирать).
Поскольку функция управления подразумевает функцию подчинения, то заметим, что глагол subordinate «подчиняться» политкорректно заменяется в английском обиходе на report (head of department reports to the managing director, MD reports to the Board).
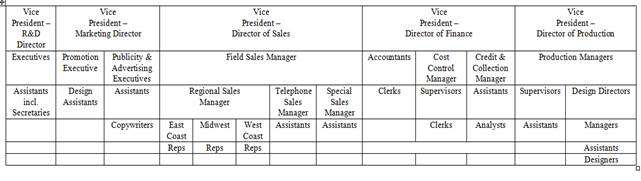
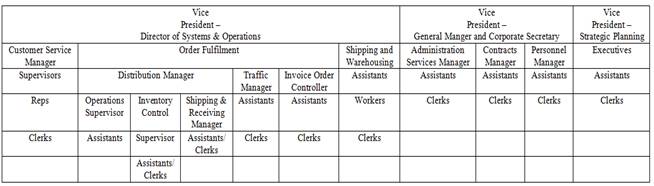
4.3. Задание: Проанализировать блок-схему, на которой представлена крупная американская корпорация. Выпишите названия отделов, подразделений, о которых пока не шла речь, параллельно составьте список должностей разного уровня.
President
Assistant to the President
РАЗДЕЛ 5. СТАТУС КОМПАНИИ: ФОРМЫ СОБСТВЕННОСТИ
1. Организационно-правовые формы: формы собственности.
Ниже мы приводим текст из образовательной энциклопедии MS EnCarta Encyclopedia на статью Forms of Business Ownership.
Задание. Ознакомьтесь со статьей (часть информации уже обсуждалась в связи с характеристикой рыночной экономики). Сделайте выписки из статьи для последующего обсуждения и сравнения представленных фактов с их аналогами в России.
There are a number of different forms of business ownership. These include
(1) sole proprietorships,
(2) partnerships,
(3) corporations,
(4) joint ventures, and
(5) syndicates.
A Sole Proprietorship The most common form of ownership is a sole proprietorship —that is, a business owned by one individual. Today there are more than 16 million sole proprietorships in the United States. These businesses have the advantage of being easy to both set up and dissolve because few laws exist to regulate them. Proprietors, as owners, also maintain direct control of their businesses and own all their profits. On the other hand, owners of proprietorships are personally responsible for all business debts and, constrained by the limits of their personal financial resources, they may find it difficult to expand or increase their profits. For those reasons, sole proprietorships tend to be small, primarily service and retail businesses.
B Partnership A partnership is an association of two or more people who operate a business as co-owners. There are different types of partners. A general partner is active in the operation of a business and is liable for all of its debts. In small businesses with only two or three owners, all will be general partners. A limited partner, by contrast, invests in a business but is not involved in its daily operations. Partnerships, like sole proprietorships, are relatively easy to establish. Furthermore, partners can pool financial resources to fund expansion, and can divide their duties and responsibilities according to personal expertise and abilities. For example, one partner may be very good at selling, while another has a knack for maintaining good financial records. As with sole proprietorships, however, partnerships may entail substantial financial risks, as all of the general partners are liable for the debts of the business. And unlike proprietorships, disagreements among partners can harm partnership businesses.
C Corporation A corporation is a legal entity that exists as distinct from the individuals who control and invest in it. As a result, a corporation can continue indefinitely through complete changes of ownership, leadership, and staffing. Current owners can sell their holdings to other individuals or, if they die, have their assets transferred to heirs. This is possible because a corporation creates shares of stock that are sold to investors. One strength of the corporate business structure is that stockholders have limited liability, as opposed to the unlimited liability of general partners, so they cannot lose more than their initial investment. Investors may also easily buy and sell stocks of public corporations through stock exchanges. By offering stock publicly, a corporation enables anyone with some money to buy th
Дата добавления: 2015-10-16; просмотров: 247 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| НАПРАВЛЕНИЕ И СКОРОСТЬ ВЕТРА 1 страница | | | Integrity |