
Читайте также:
|
Coursework 14 2012
Mass of proton = 1.67×10-27 kg µ0 = 1.26 × 10-6 H m-1
Charge on an electron = - 1.6×10-19 C mass of electron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg
1 u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
1) An electron enters a magnetic field of magnitude 0.750 T with a velocity of
2.00 × 107 m s-1 at an angle of 30° to the field. Evaluate the force on the electron. The following diagram shows the relative directions of the electron’s velocity (the thick arrow) and the B field (the set of parallel arrows). What is the direction of the force on the electron?
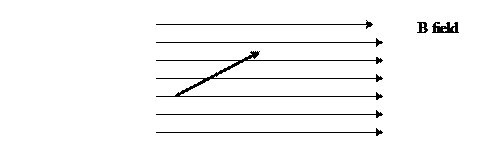
(3 marks)
2) A proton has a speed of 5.00 × 106 m s-1 and is passing through a region of magnetic field B of magnitude 3.00 × 10-3 T. The proton’s velocity is indicated by the arrow and is perpendicular to the field direction as shown in the diagram below.

Find the magnitude of the force on the proton. Show that the path of the proton in the field is circular. Copy the above diagram and draw the circular path of the proton. Find the radius of the circle. (6 marks)
3) Two long parallel wires are separated by a distance of 0.600 cm. One wire carries a current of 2.00 A and the other a current of 3.00 A. The currents are in the same direction.
a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force per metre on each wire.
b) How far from the wire carrying 2.00 A will the magnetic field be equal to zero?
(5 marks)
4) Two long straight wires perpendicular to the plane of the page carry equal but opposite currents of 5.00 A as shown below.
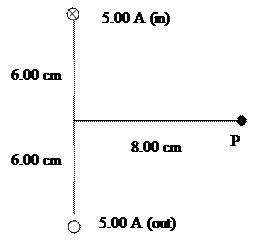 |
a) Find the magnetic field strength at point P.
b) What force per metre length would a long straight third wire experience if placed at P such that it is perpendicular to the plane of the paper and carries a current of 3.00 A out of the plane of the paper.
(6 marks)
5) The magnetic field B at a certain point on the Earth’s surface has a horizontal component of 18.0 μT due north, and a vertical component of 55.0 μT downwards. Calculate the force on a 1.00 m length of straight wire carrying a current of 4.00 A. when:
a) the wire is vertical with the current flowing downwards;
b) the wire is horizontal with the current in the direction from east to west.
(4 marks)
6) In a cathode ray oscilloscope the electrons pass through two parallel metal plates as shown.
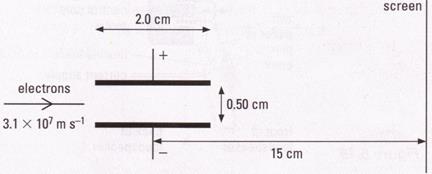
There is a potential difference of 80 V between the plates. Electrons are accelerated between a cathode and anode before entering the plates with a velocity of
3.10 × 107 m s-1.
a) Find the acceleration of the electrons along the E field direction
b) Evaluate the time each electron takes to pass between the plates
c) Find the component of the velocity of the electron along the field direction just as it leaves the region between the plates (ie its vertical component).
d) Estimate the deflection of the electron beam on the screen caused by the 80 V applied voltage across the plates.
(8 marks)
7) The diagram below shows a narrow beam of electrons entering symmetrically between a pair of parallel metal sheets. There is a uniform magnetic field B of 0.020 T between the plates and the relative directions are as shown. When a potential difference of 3.5 kV is applied across the plates the electron beam is undeviated as it passes through the plates.
Calculate the speed of the electrons.
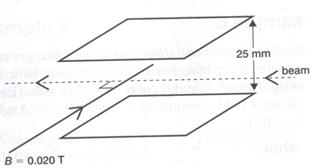
(2 marks)
8) In the diagram below an electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 500 V and then injected into a region of uniform magnetic field. Once in the magnetic field it completes half a revolution in 2.00 ns.
a) Find the speed of the electron as it enters the magnetic field
b) Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B
c) Determine the radius of the semicircle.
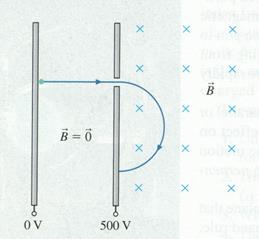
(6 marks)
9) In a mass spectrometer, ions first pass through the crossed electric (E) and magnetic (B) fields of a velocity selector where E = 3.0 × 105 V m-1 and B = 0.40 T.
They are then deflected by a magnetic field which causes the ions to take a semi-circular path before arriving at a photographic plate.
If this magnetic field is also 0.40 T find the difference in position on the photographic plate for singly charged ions of the carbon isotopes C12 and C14. (5 marks)
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 116 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Coursework 13: Electric and Gravitational Forces and Fields | | | Стартовий код |