
|
Читайте также: |
1) Describe under what conditions waves from two sources produce an interference minimum. Your answer should mention the wavelength, phase and spacing of the sources, as well as path difference. (4 marks)
2) a) The diagram below shows two coherent sources of microwaves with wavelength 4 cm. The distance S1X is 25 cm and distance S2X is 31 cm. State with reasons whether the superposition of waves at X is constructive or destructive.
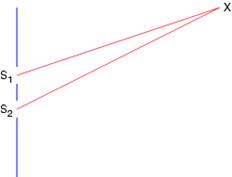
b) Along what line is the interference from the two sources always constructive regardless of the wavelength? (4 marks)
3) The graph below shows the displacement of particles in a transverse progressive wave plotted against the distance x from the source at a particular instant. Sections of the curve have been labelled A, B, C, D, and E.
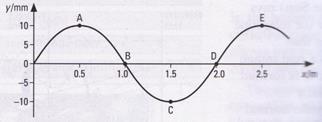
i) Write down the letters of
a. all the points at which the speed of the particle is a maximum
b. all the points at which the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle is a maximum.
c. two points which are in phase
d. two points which are 900 out of phase (4 marks)
ii) State the amplitude and wavelength of the wave. (2 marks)
4) What is the effect on the interference pattern produced in a Young’s slit experiment if each of the following changes are made while holding all other parameters constant
i) the wavelength is increased
ii) the slit separation is decreased
iii) the distance from slits to screen is increased?
Explain what is observed on the screen if one of the slits is covered up.
(4 marks)
5) Find the amplitude, period, frequency, wave velocity and wavelength for the wave given by
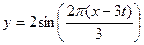
(5 marks)
a) On the same set of axes sketch curves to show the displacement y of this wave as a function of x for t = 0 and t = 0.5 s. (2 marks)
b) On another set of axes sketch curves representing the displacement y of this wave as a function of t for x =0 and x =0.75 s (2 marks)
6) A simple harmonic wave of wavelength 16 cm and amplitude 2.5 cm is propagating along a string in the negative x direction at 35 cm s-1. Obtain a mathematical expression describing the displacement y of the string as a function of time and x-position. (4 marks)
For any particle in the string find i) the maximum speed ii) the maximum acceleration. (4 marks)
7) The equation of a transverse wave travelling along a stretched string is:
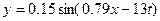
where distances are in metres and time in seconds.
a) What is the displacement of a particle in the string at x =2.3 m, t = 0.16 s?
b) What is the speed of the wave?
c) What is the frequency of the motion of a particle in the string? (6 marks)
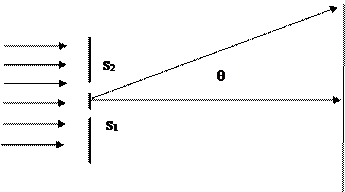
8) The diagram below shows parallel monochromatic light emitted by a laser incident normally on a pair of slits as in the Young’s slit experiment.
 | |||
| |||
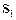 and
and 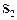 are slits at right angles to the plane of the diagram. When illuminated by light from the laser they form coherent sources of light and an interference pattern is formed on the screen.
are slits at right angles to the plane of the diagram. When illuminated by light from the laser they form coherent sources of light and an interference pattern is formed on the screen.
a) Show that interference maxima occur along directions given by:
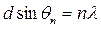
where d is the slit spacing and n is an integer. (2 marks)
b) Use this result to show that, under certain conditions, the spacing of interference fringes on the screen is given by:
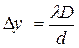 (2 marks)
(2 marks)
c) Suppose the wavelength of light is 620nm, the distance D is 0.8m, and the slit separation d is 0.05 mm. What is the fringe separation? (2 marks)
d) When the laser is replaced by a white light source a spectrum is produced on each side of a central bright white fringe. Visible white light contains all wavelengths in the range 400nm to 780nm. Calculate the width on the screen of the first order white light spectrum. (2 marks)
9) In a Young’s slit experiment using a white light source the slit separation is 0.68 mm and the distance from the slits to the screen is 0.80 m. Describe the fringe pattern observed on the screen. Show that the sixth green fringe (wavelength 500 nm) from the central maximum coincides with the fifth orange fringe (wavelength 600 nm). (4 marks)
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 159 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Structural types of the sentences in English and Ukrainian | | | ЖЕНСКИЕ, РОССИЙСКИЕ ПЕСНИ |