
|
Читайте также: |
Campylobacteriosis
Campylobacteriosis is an infection by the campylobacter bacterium [1], most commonly C. jejuni. It is among the most common bacterial infections of humans, often a foodborne illness. It produces an inflammatory, sometimes bloody, diarrhea or dysentery syndrome, mostly including cramps, fever and pain.
Edit] Cause
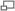
Campylobacter bacteria are the number-one cause of food-related gastrointestinal illness in the United States. This scanning electron microscope image shows the characteristic spiral, or corkscrew, shape of C. jejuni cells and related structures.
Main article: Campylobacter
Campylobacteriosis is caused by Campylobacter organisms. These are curved or spiral, motile, non–spore-forming, gram-negative rods. This is most commonly caused by C. jejuni, a spiral and comma shaped bacterium normally found in cattle, swine, and birds, where it is non-pathogenic. But the illness can also be caused by C. coli (also found in cattle, swine, and birds) C. upsaliensis (found in cats and dogs) and C. lari (present in seabirds in particular).
One cause of the effects of campylobacteriosis is tissue injury in the gut. The sites of tissue injury include the jejunum, the ileum, and the colon. C jejuni appears to achieve this by invading and destroying epithelial cells.
Some strains of C jejuni produce a cholera-like enterotoxin, which is important in the watery diarrhea observed in infections. The organism produces diffuse, bloody, edematous, and exudative enteritis. In a small number of cases, the infection may be associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura through a poorly understood mechanism.
edit] Transmission
The common routes of transmission for the disease-causing bacteria are fecal-oral, person-to-person sexual contact, ingestion of contaminated food (generally unpasteurized (raw) milk and undercooked or poorly handled poultry), and waterborne (ie, through contaminated drinking water). Contact with contaminated poultry, livestock, or household pets, especially puppies, can also cause disease.[2] Animals farmed for meat are the main source of campylobacteriosis. A study published in PLoS Genetics (September 26, 2008) by researchers from Lancashire, England, and Chicago, IL, found that 97 percent of campylobacteriosis cases sampled in Lancashire were caused by bacteria typically found in chicken and livestock. In 57 percent of cases, the bacteria could be traced to chicken, and in 35 percent to cattle. Wild animal and environmental sources were accountable for just three percent of disease.[3]
The infectious dose is 1000-10,000 bacteria (although ten to five hundred bacteria can be enough to infect humans). Campylobacter species are sensitive to hydrochloric acid in the stomach, and acid reduction treatment can reduce the amount of inoculum needed to cause disease.
Exposure to bacteria is often more common during travelling, and therefore campylobacteriosis is a common form of travelers' diarrhea.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-30; просмотров: 154 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Ночная школа — 3 | | | Capítulo 1 |