
|
Читайте также: |
 Let’s examine the engagement ladder in Figure 7.1 for a moment before we move to the subject of conversations. I have always used this as a way of thinking about culture change, which really is about encouraging employees to make the choices that change one set of behaviours to the ones needed for performance improvement.
Let’s examine the engagement ladder in Figure 7.1 for a moment before we move to the subject of conversations. I have always used this as a way of thinking about culture change, which really is about encouraging employees to make the choices that change one set of behaviours to the ones needed for performance improvement.
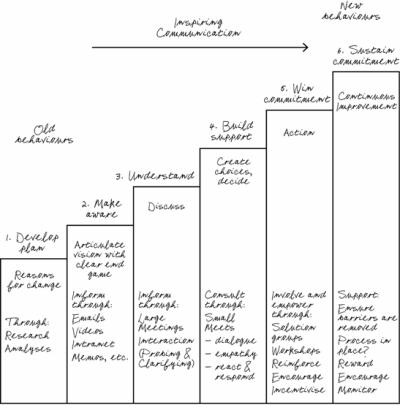
 Figure 7.1: The engagement ladder
Figure 7.1: The engagement ladder
 The first stage of any change process is that of coming to the realization that change is needed. Developing a strategy is beyond my purview for this book, so let’s move quickly to Stage 2 (Figure 7.1). This is where you have decided on your plan, which now needs to be communicated. Through publications, memos, videos and e-mails, you can create awareness of the need for change and the fact of change. Through written means, this is all you will achieve. You will not have got close to the buy-in you need to deliver new behaviours. The third step is to ensure people truly understand what has to happen and why, and get them to participate in deciding what to do. But for people to truly understand what is necessary and what is coming, you need to stand in front of people and allow them to question and probe. People don’t always hear what you’re saying. They listen through a filter of their own views, prejudices, fears and perspectives, and their take-out may be very different from your message. Unless you have checked what they are hearing, given them a chance to clarify, then you cannot be sure that you have communicated.
The first stage of any change process is that of coming to the realization that change is needed. Developing a strategy is beyond my purview for this book, so let’s move quickly to Stage 2 (Figure 7.1). This is where you have decided on your plan, which now needs to be communicated. Through publications, memos, videos and e-mails, you can create awareness of the need for change and the fact of change. Through written means, this is all you will achieve. You will not have got close to the buy-in you need to deliver new behaviours. The third step is to ensure people truly understand what has to happen and why, and get them to participate in deciding what to do. But for people to truly understand what is necessary and what is coming, you need to stand in front of people and allow them to question and probe. People don’t always hear what you’re saying. They listen through a filter of their own views, prejudices, fears and perspectives, and their take-out may be very different from your message. Unless you have checked what they are hearing, given them a chance to clarify, then you cannot be sure that you have communicated.
 To build support for the change programme, you move to Stage 4– where smaller meetings are needed in which people can talk about how they feel about the changes, often simply to vent, but from here you can start talking with people about the new behaviours and what they mean. This is the stage where you finally persuade people of the need for change and focus them on what is needed. You have to make it understood. Do people know about the problem? Do they know about their own behaviours? Do they understand what’s necessary? Do they believe change is necessary or relevant to them? Encourage acceptance.
To build support for the change programme, you move to Stage 4– where smaller meetings are needed in which people can talk about how they feel about the changes, often simply to vent, but from here you can start talking with people about the new behaviours and what they mean. This is the stage where you finally persuade people of the need for change and focus them on what is needed. You have to make it understood. Do people know about the problem? Do they know about their own behaviours? Do they understand what’s necessary? Do they believe change is necessary or relevant to them? Encourage acceptance.
 In order to win their commitment and change their behaviours, you have to move to Stage 5, and have the powerful conversations that allow them to offer up their ideas, and make the choices to which they commit themselves, and empower them to get on with things. This is where conversations are most powerful and most needed.
In order to win their commitment and change their behaviours, you have to move to Stage 5, and have the powerful conversations that allow them to offer up their ideas, and make the choices to which they commit themselves, and empower them to get on with things. This is where conversations are most powerful and most needed.
 However, sustaining commitment to the new behaviours means that you have to be constantly removing barriers to change, responding to suggestions, making sure that the support structures are in place and that the teams have the resources and skills they need, as you can see in Stage 6. You have to reward the right behaviours, offer constant encouragement and recognition, make heroes of those who display exemplary behaviours, measure outcomes and feed that back to people to stimulate continuous improvement.
However, sustaining commitment to the new behaviours means that you have to be constantly removing barriers to change, responding to suggestions, making sure that the support structures are in place and that the teams have the resources and skills they need, as you can see in Stage 6. You have to reward the right behaviours, offer constant encouragement and recognition, make heroes of those who display exemplary behaviours, measure outcomes and feed that back to people to stimulate continuous improvement.
 I call this approach FIDAR – find and define, align and refine. When planning your own communications, think about how you phase the communications along these lines. Most leaders I talk to, at this stage, balk at the length of time this process looks like it’s going to take. They wanted to simply tell people and get on with things. This impatience is a killer. Successful leaders know that they have to take the time to have these powerful conversations, because this is the only way of ensuring a speedy and successful change programme.
I call this approach FIDAR – find and define, align and refine. When planning your own communications, think about how you phase the communications along these lines. Most leaders I talk to, at this stage, balk at the length of time this process looks like it’s going to take. They wanted to simply tell people and get on with things. This impatience is a killer. Successful leaders know that they have to take the time to have these powerful conversations, because this is the only way of ensuring a speedy and successful change programme.
 Successful change comes from a real understanding of people, their habits and their motivations (see Chapter 8.) First you have to look at barriers: what are the things that stop people from adopting a new behaviour? Then you need to consider the triggers. How can you get people to start a new behaviour? Finally you have to consider the motivators – the ways to help people stick with new behaviours.
Successful change comes from a real understanding of people, their habits and their motivations (see Chapter 8.) First you have to look at barriers: what are the things that stop people from adopting a new behaviour? Then you need to consider the triggers. How can you get people to start a new behaviour? Finally you have to consider the motivators – the ways to help people stick with new behaviours.
 Using this method will greatly increase the likelihood of delivering successful behaviour change. Simply broadcasting at people, instructing, imploring and exhorting, is very unlikely to deliver the changes required – yet this is most often the preferred methodology of many leaders.
Using this method will greatly increase the likelihood of delivering successful behaviour change. Simply broadcasting at people, instructing, imploring and exhorting, is very unlikely to deliver the changes required – yet this is most often the preferred methodology of many leaders.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 154 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Choice over change, any day of the week | | | The right process |