
| 1.Translate the following definitions and memorize the terms: |
| amplification (n) - | the increase in strength of an electrical signal (by means of an amplifier); |
| amplitude (n) - | the maximum variation from the zero or mean value of a periodically varying quantity |
| capacitor (n) - | a device for accumulating electric charge, usually consisting of two conducting surfaces separated by a dielectric |
| circuitry (n) - | the design of an electrical circuit; the system of circuits used in an electronic device |
| current (n) - | a flow of electric charge through a conductor |
| discard (v) - | to get rid of as useless or undesirable |
| feedback (n) - | the return of part of the output of an electronic circuit, device, or mechanical system to its input, so modifying its characteristics. Can be negative or positive. b) that part of the output signal fed back into the input |
| frequency (n) - | the number of times that a periodic function or vibration repeats itself in a specified time, often 1 second. It is usually measured in hertz. |
| inductance (n) - | the property of an electric circuit as a result of which an electromotive force is created by a change of current in the same circuit or in a neighbouring circuit |
| input (n) - | the signal or current fed into a component or circuit |
| interference (n) - | any undesired signal that tends to interfere with the reception of radio waves |
| loop (n) - | a closed electric or magnetic circuit through which a signal can circulate |
| modulation (n) - | the act or process of superimposing the amplitude, frequency, phase, etc., of a wave or signal onto another wave (the carrier wave) or signal or onto an electron beam |
| oscillation (n) - | regular fluctuation in value, position, or state about a mean value, such as the variation in an alternating current or the regular swinging of a pendulum |
| receiver (n) - | the equipment in a telephone, radio, or television that receives incoming electrical signals or modulated radio waves and converts them into the original audio or video signals |
| amplifier (n) - | an electronic device used to increase the strength of the signal fed into it |
| amplitude modulation (AM, am) (n) - | one of the principal methods of transmitting audio, visual, or other types of information using radio waves, the relevant signal being superimposed onto a radio-frequency carrier wave. The frequency of the carrier wave remains unchanged but its amplitude is varied in accordance with the amplitude of the input signal |
| conductor (n) | a substance, body, or system that conducts electricity, heat, etc. |
| current (n) - | a flow of electric charge through a conductor (the rate of flow of this charge); it is measured in amperes |
| diode (n) - | a semiconductor device containing one p-n junction, used in circuits for converting alternating current to direct current |
| frequency modulation (FM (n) - | a method of transmitting information using a radio-frequency carrier wave. The frequency of the carrier wave is varied in accordance with the amplitude and polarity of the input signal, the amplitude of the carrier remaining unchanged |
| input (n) - | the signal or current fed into a component or circuit |
| integrate (v) - | to make or be made into a whole; incorporate or be incorporated |
| microchip (n) - | a small piece of semiconductor material carrying many integrated circuits; chips, -chipping, -chipped |
| modulation (n) - | the act or process of superimposing the amplitude, frequency, phase, etc., of a wave or signal onto another wave (the carrier wave) or signal or onto an electron beam |
| relay (n) - | a combination of a receiver and transmitter designed to receive radio signals and retransmit them, in order to extend their range |
| semiconductor (n) - | a substance, such as germanium or silicon, that has an electrical conductivity that increases with temperature and is intermediate between that of a metal and an insulator |
| sequence (n) - | a successive order of two or more things: chronological sequence; an action or event that follows another or others |
| transistor (n) - | a semiconductor device, having three or more terminals attached to electrode regions, in which current flowing between two electrodes is controlled by a voltage or current applied to one or more specified electrodes. The device is capable of amplification, etc., and has replaced the valve in most circuits since it is much smaller, more robust, and works at a much lower voltage |
| fluctuation (n) - | change, especially continuous and between one level or thing and another: fluctuations in share prices/the exchange rate/temperature. |
| constant (adj)- | staying the same, or not getting less or more: We've kept up a fairly constant speed. |
| require (v) - | to need or make necessary: Please telephone this number if you require any further information. |
| alternate (adj) - | with first one thing, then another thing, and then the first thing again: a dessert with alternate layers of chocolate and cream. |
| receive (v) - | (of a radio or television) to change signal into sounds and pictures. |
| range (n) - | the distance within which you can see, hear. |
| deviation (n) - | different direction. |
| broadcast (v) - | to send out a programme on television or radio: Radio Caroline used to broadcast from a boat in the North Sea. |
| subtract (v) - | to remove a number from another number: Four subtracted from ten equals six. |
| satellite (n) - | an artificial object sent up into space to travel round the earth, used for collecting information or communicating by radio, television, etc: The World Cup was transmitted around the world by satellite. |
| modulation (n) - | the act or process of superimposing the amplitude, frequency, phase, etc., of a wave or signal onto another wave (the carrier wave) or signal or onto an electron beam. |
| subcarrier(n) - | a carrier wave modulated by a signal wave and then used with other subcarriers to modulate the main carrier wave. |
| multiple (adj) - | numerous and often varied |
| fidelity (n) - | the degree of exactness with which something is copied or reproduced. |
| cause (v) - | make (something) happen |
| access (n) - | the right or opportunity to use or benefit from something: Do you have access to a computer? |
| allocation (n) - | the action or process of allocating or distributing something; location, disposition, placement; |
| apart (adv) - | separated by a distance or, less commonly, by time: How far apart should the speakers be placed? |
| assign (v) - | (often passive) to choose someone (something) to do a particular job: Which frequency was assigned to this transmission? |
| burst (n) - | an instance of breaking or splitting; a break, breach, rupture; |
| carrier (n) - | a high-frequency electromagnetic wave modulated in amplitude or frequency to convey a signal; |
| cellular (adj) - | denoting or relating to a mobile telephone system that uses a number of short-range radio stations to cover the area that it serves, the signal being automatically switched from one station to another as the user travels about; |
| coverage (n) - | the area reached by a particular broadcasting station or advertising medium: A network of eighty transmitters would give nationwide coverage. |
| entity (n) - | something which exists apart from other things, having its own independent existence: A GSM network is composed of several entities with specific interfaces. |
| node (n) - | 1) a point at which lines or pathways intersect or branch; a central or connecting point; 2) a piece of equipment, such as a PC or peripheral, attached to a network; |
| link (n) - | a means of contact by radio, telephone, or computer between two points: This stream is too high to be transmitted over a radio link. |
| perform (v) - | to do an action or piece of work: Computers perform a variety of tasks. |
| range (n) - | the maximum distance at which a radio transmission can be effectively received; |
| stand for (v) - | to represent, to mean something: QAM stands for quadrature amplitude modulation. |
| subscriber (n) - | someone who subscribes to a product, service or organization (pays money so that a newspaper or magazine is regularly sent to him): The cable television company has launched five new channels to increase its number of subscribers. |
| transceiver (n) - | a device that can both transmit and receive communications, in particular a combined radio transmitter and receiver. |
| acceptance (n) - | agreement that something is right or true: His ideas soon gained acceptance from scientists (= became approved of). |
| actuator (n) - | device that makes a machine work, puts into action or mechanical motion (switch); |
| consumption (n) - | the amount of energy (electricity, gas, oil) that is used: We need to reduce the power consumption of this device. |
| detector (n) - | a sensing device used to find particular substances or things, or measure their level: a metal/smoke detector; |
| device (n) - | an object or machine which has been invented to fulfil a particular purpose: Rescuers used a special device for finding people trapped in collapsed buildings. |
| embedded (adj) - | inserted as an integral part of a surrounding whole, integrated; |
| headset (n) - | a set of headphones, especially one with a microphone fixed to it; |
| node (n) - | an interconnection point on a network; |
| proximity (n) - | the state of being near in space or time: The best thing about the location of the house is its proximity to the town center. |
| router (n) - | a device that forwards data packets to the appropriate parts of a computer network; |
| sense (v) - | to acquire information about an object or phenomenon, to test, to detect; |
| short-range (adj) - | reaching a short distance: short-range antenna. |
| simultaneously - (adv) | happening or done at the same time that something else. This program was broadcast on TV and radio simultaneously. |
| spacing (n) - | the arrangement of objects in a space; |
| tracking (n) - | the act or process of following something or someone; |
| uniform (adj) - | the same, not varying or different in any way: In these offices the walls and furniture are a uniform grey. |
to define – to say what the meaning of something, especially a word, is: In this dictionary 'reality' is defined as 'the state of things as they are, rather than as they are imagined to be'.
domain – an area of interest or an area over which a person has control: She treated the business as her private domain. These documents are in the public domain
application – a way in which something can be used for a particular purpose: The design has many applications. The application of this research in the treatment of cancer...
to implement – to put a plan or system into operation: The changes to the national health system will be implemented next year.
approximation – a guess of a number that is not exact but that is close: Could you give me a rough approximation of how many people will be coming? What he said bore no approximation whatsoever to the truth (= was not at all like the truth).
bandwidth – 1) the amount of information that can be sent between computers, through a telephone wire, etc: The system will handle not only telephone calls and data messages but other signals that need high bandwidth, for instance those that encode TV pictures. 2) the range of frequencies used to send information over a distance using telephone wires.
cell – a small part of something: the cells of a honeycom.
jitter –vibration
flawlessly – perfectly or without mistakes
robust – (of an object or system) strong and unlikely to break or fail: a robust pair of walking boots; a robust economy
to convert - to change or adapt the form, character, or function of; transform.
to shrink – to become or make smaller in size or amount.




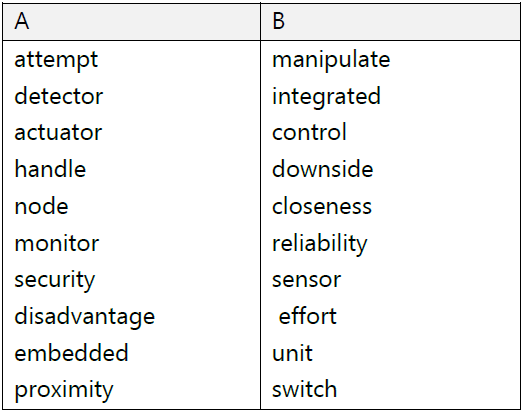


3. Match a verb in A with a noun or a word combination in B:
| A | B | A | B |
| mechanical vacuum current gallium copper logic electronic | arsenide components flow gates relay tube wire | spared integrated to mimic hi-fidelity a score search complex | behavior circuit data from of transistors sound |
| A | B | A | B |
| amplitude radio capture spark digital long subcarrier transmitter | channel messaging spectrum signal fibre effect modulation range | analog telecommunication optical snowy instant high strong single | interference fidelity sideband voice systems pictures data services frequency |
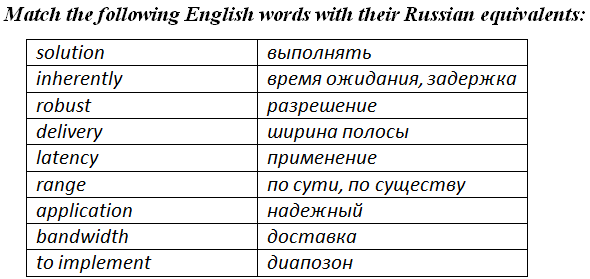
4. Match the following words with their equivalents in Russian:
| amplifier circuitry current feedback feeder frequency inductance in-phase loop oscillation | электрический ток волновод, фидер индуктивность; индукция, колебание; катушка индуктивности компоновка схем (схемотехника) контур, виток, рамка обратная связь синфазный усилитель частота, периодичность |

| to subtract fluctuation source constant to contain subcarrier sub-band narrowband broadcast spectrum retune network | содержать, вмещать поддиапазон сеть диапазон узкополосный постоянный вычитать перенастраивать источник колебания поднесущая транслировать |
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 104 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Quotes About Ecology | | | Источник универсального параметра |