
Basic types of smog
1) Photochemical smog
- action of sunlight on hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides in the air.
Smog components =chemicals released as waste from cars and industrial processes.
-When activated by the right amount of sunlight, the compounds go through a chemical reaction that produces gases called oxidants.
-Ozone forms the most common oxidant in photochemical smog.
- Other oxidants in smog include nitrogen dioxide and peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN).
2) London-type smog
- occurs when water droplets in the air condenses on smoke particles produced by the burning of coal, forming tiny smog droplets.
-dangerous part of London smog is sulfur dioxide: gas that attacks the lungs and makes breathing difficult è London- type smog is sometimes called sulfur smog.
Great Smog, befell in London in Dec 1952: death of thousands of Londoners due to respiratory tract problems, hypoxia (low level of oxygen in of blood).
Photochemical Smog in LA, California
Thermal Inversion
• Cities adjacent to mountains or in valleys tend to have photochemical smog because pollutants are trapped by thermal inversions.
• Thermal inversions occur when warm air becomes sandwiched between two layers of cold air and acts like a lid on a valley.
• Warm air cannot rise, causing smog accumulation.
• Almaty – city of thermal inversion
Thermal inversion occurs when a layer of warm air settles over a layer of cooler air that lies near the ground. The warm air holds down the cool air and prevents pollutants from rising and scattering.
Smog in Almaty: Thermal Inversion
Almaty
Thermal inversion:
The warm air holds down cool air and prevents pollutants from rising and scattering.
Inversion layer is defined as the layer of the atmosphere in which the temperature is increasing.
Hazardous Air Pollutants
• Toxic substances may be hazardous air pollutants that harm human health or damage the environment:
• 5 groups based on their adverse impact on human health:
Carcinogens, neurotoxins, mutagens, teratogens, allergens.
(see lecture #6)
• Air pollutants that are toxic substances (examples):
- Lead: neurotoxin and criteria air pollutant;
- Tobacco smoke: carcinogen and air pollutant;
- Paint: allergen and air pollutant
Dioxins - poisonous chemicals, containing C, H, O, chlorine. They occur as natural byproducts from forest fires, industrial: incineration (сжигание мусора), paper and pulp bleaching (отбелка целлюлозы), exhaust emissions.
The largest sources of dioxins: trash burning and forest fires.
Dioxins are ubiquitous in the environment.
Dioxin is human carcinogen. High levels of dioxin— cause skin condition chloracne. Other adverse effects: excessive body hair and other skin lesions: rash, discoloration.
Control of Air Pollution
• Motor vehicles are the primary source of major air pollutants: carbon monoxide, VOCs, nitrogen oxides.
• Ozone is a secondary pollutant of automobile use.
• Emission Control resulted in improvement in air quality worldwide (next slide).
– CO, VOCs, SO2, PM declined
– NOX did not decrease (people drive more).
– Lead dropped sharply (not used for increasing octane number)
1 слайд
Air Quality in the World
• Over the past 20 yrs, developed countries made progress in improving air quality.
• But in the developing world air quality has been getting worse.
• Euro standards - car emission standards:
• Euro 1 (catalysts)
• Euro 2, 3, 4, 5
Developed countries greatly increased air quality and reduced air pollution, through enforcement of the legal acts. Many countries followed programs for improving air quality as well. Unfortunately, in most cases, the less developed countries of the world have been unable to produce and enforce reasonable standards of air quality within their countries. Lower air pollution standards, in general, are one reason why companies that produce substantial amounts of pollution have sometimes moved their operations to less developed countries to save money.
Euro standards in Kazakhstan
• Euro II standard in Kazakhstan since 2009
• Euro III should start in Kazakhstan in Jan 2013
• Euro standard implies:
– Engine quality
– Fuel quality
• Most European countries at Euro IV level.
• European standards are more stringent as compared with other countries.
Euro standards impose restrictions on age of the cars to be imported:
Euro II – ≤ 12 yrs old
Euro III – ≤ 10 yrs old
Acid Rain, Acid Deposition
• Acid rain is a worldwide problem.
• Acid rain has pH < 5.6
• Acid rains have concentrations of acids ~1000 times higher than normal.
• Harmful effects of acid rain:
1) Property and structural damage
• Limestone degradation
2) Damage to forests
• Acidic soil results in reduced nutrient absorption
3) Lake acidification à food chain disruption
• Acid deposition is the accumulation of potential acid-forming particles on a surface.
2 слайдыЮвторой слайд есть рисунок а ниже идет описание!
Acid Rain impact
This statue, crafted in medieval times, remained intact for several hundred yrs. However, with the industrial development, and increasing acidity in the rainfall, the surface has eroded severely in the last few decades.
Ozone Depletion
• In 1985: discovered a significant thinning of the ozone layer over the Antarctic in Southern Hemisphere:
– “ozone hole.”
• Ozone in stratosphere shields the Earth from harmful UV radiation.
• Chlorofluorocarbons are strongly implicated in the ozone reduction in the upper atmosphere.
Adverse Effects of Air Pollutants
• Sulfur dioxide - acid rain, health damage, visibility reduction
• Nitrogen oxides - acid rain, health damage, eutrophication*), growth of weedy species
• Carbon monoxide - inhibited respiration
• Lead and mercury - neurological damage
• Chlorofluorocarbons - ozone depletion
• Particulate matter - lung damage, cancer
• Volatile Organic Compounds VOCs – carcinogenic;
*) Waters rich in mineral / nutrients promote growth of algae, which reduces the amount of O2 è extinction of species.
Major types of air pollutants: sulfur dioxide, which most important component of acid rain, nitrous oxides, which add substantial nitrogen input into ecosystems, carbon monoxide, which adversely impacts human health, lead and mercury, which cause neurological damage in humans and potentially similar effects in animals, chlorofluorocarbons, which impact the ozone layer, particulates and volatile organics.
Air Pollution Level
• Highest in the cities and industrial centers
• 1)* Shymkent – the most polluted city
• 2) Temirtau
• 3) Almaty – the 3d place
• Ust-Kamenogorsk (Ridder, Zyryanovsk), Taraz, Jezkazgan register the high levels
*) – Feb 2012, ecolog. Data
• Major pollution sources in Kazakhstan:
– Non-ferrous metallurgy
– Thermal Power Plants
– Oil & gas extraction
– Motor vehicles
Air Pollutants in Kazakhstan
• Main pollutants:
• Dust, sulfur and nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, lead, benzapyrene, formaldehyde, cadmium, iron, mercury and fluoric acid.
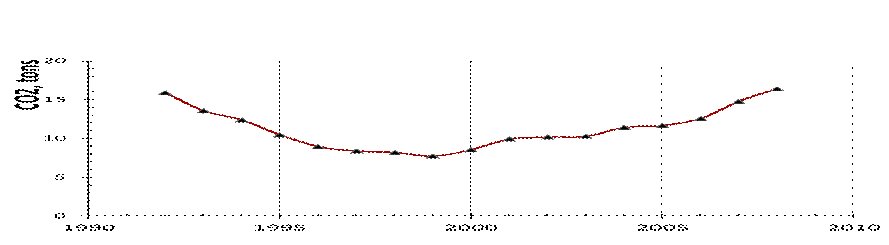
CO2 per capita Emissions in Kazakhstan
Criteria of Air Quality: MAC, IAP
• MAC - Maximum Admissible Concentration
• IAP (Index of Air Pollution) – composite index
• Observation posts in 20 major cities of Kazakhstan (Kazhydromet)
• Pollutants measured: carbon monoxide, PM, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, phenol and formaldehyde.
• Contribution of auto emissions to the air pollution reached ~ 60% in recent years
– In Almaty - ~80% of air pollution by cars
Lead metal emitted into the air as small particles (car & industrial emission

Indoor Air Pollution
• Outdoor air pollution – main attention
• Anti-tobacco campaigns
• Smoking - related diseases are responsible for 18% of deaths in Kazakhstan
• Second-hand smoke
• 90% of their lives people spend indoors
• Poor ventilation, heating and cooking fires in rural area
In many cases, sources of air pollution inside home, including chloroform, benzene, formaldehyde, and smoke cause more health problems that pollution outside. One of major reasons that smoking has been banned in many public building, including Kazakhstan and KIMEP, is due to the adverse health impacts of the smoke within public buildings. Though this probably doesn't have much impact on the improvement of health of actual smokers, it probably eliminates the adverse impact on nonsmokers, which is substantial.
Effects of Air Pollution
• Human health
• Plant pathology
• Visibility reduction
• Acid deposition
Air pollution is likely just as serious for ecosystem health as it is for human health, though less is known about pollution impacts on ecosystems since much more money and effort is spent studying human health. Effects include impacts on plants, and thus impacts on all animals that require those plants and other animals as a source of food. The reduction of visibility in air is also a problem that is studied particularly because of the impact on human recreation.
Ecosystem damage caused by acid rain
Atmospheric deposition of pollutants is a serious local and regional problem in some areas of the world. For instance, this picture shows the impact of SO2 emissions near lake Ontario, on local forests. Essentially all of the native vegetation has been destroyed, and soil has eroded down to bedrock in many areas. The installation of air pollution control equipment has greatly reduced emissions from the smelters recently, and many of the local ecosystems are beginning to recover.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-23; просмотров: 124 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Most Common Cancers in the world | | | Часть 6: подготовка и вечер |