
|
Читайте также: |
· Root Mean Square – average of the squares of the velocities of molecules of the gas
· Vapor Pressure – the vapor of a liquid formed at any temperature that exerts a pressure
· Saturated Vapor Pressure (SVP) – the pressure exerted by a vapor in a closed space at a given temperature is a maximum at that temperature
· Unsaturated Vapor Pressure – the pressure applied by a vapor in a closed space at a given temperature is less than its SVP at that temperature
· Surface Tension – tendency of the surface of a liquid to contract in area and thus behave like a stretched elastic membrane
· Capillary Effect – the rise of a liquid in a fine, hollow tube or in a narrow space
· Temperature – a measure of the kinetic energy of the molecules in a material
· Thermal Physics – is the study of the macroscopic effects of the microscopic molecules
· Molecular Kinetic Theory – analysis of matter in terms of atoms in continuous random motion
· Basic Postulates of Kinetic Theory:
o There are a large number of molecules moving in random directions with variety of speeds.
o The molecules are, on the average, far apart from one another.
o The molecules are assumed to obey the laws of classical mechanics and are assumed to interact with one another only when they collide.
o Collisions with another molecule or the wall of the container are assumed to be perfectly elastic.
· Boyle’s Law – states that the pressure of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature
· Charles’ Law – states that the volume of a fixed mass of gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its absolute (Kelvin) temperature (this is the ENGLISH definition)
· Gay–Lussac’s Law – states that the pressure of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume is directly proportional to its absolute (Kelvin) temperature (this is the ENGLISH definition)
· Equation of State – pV = nRT (n = number of moles)
· Work Done – a macroscopic transfer of energy from the gas to the surroundings; W = PΔV
· Isobaric Process – a process in which the gas expands or contracts at constant pressure.
· Isochoric or Isovolumic Process – a process in which the volume of the gas stays fixed. Note that NO WORK is done on or by the gas in this process
· Isothermal Process – a process in which the temperature of the system remains constant
·  Adiabatic Process – process during which the gas does not absorb or give out any thermal energy, so Q (heat) = 0
Adiabatic Process – process during which the gas does not absorb or give out any thermal energy, so Q (heat) = 0
· Thermodynamics – macroscopic study of the behavior of systems; It was a mathematical theory developed before a detailed understanding of the particulate nature of gases
· Thermodynamic System – a macroscopic aspect of a problem than can be considered as a separate whole
·  Thermodynamic Surroundings – everything in the problem outside the thermodynamic system
Thermodynamic Surroundings – everything in the problem outside the thermodynamic system
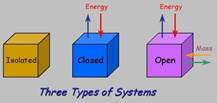
· Isolated System – no exchange of matter and heat
· Closed System – no exchange of matter but can exchange heat energy
· Open System – matter and heat can be exchanged
· Heat – an amount of thermal energy transferred from the surroundings to an ideal gas; It is a result of a temperature difference
·
· Internal Energy – energy due to the intermolecular potential energy PE and kinetic energy KE of the molecules
· 1st Law of Thermodynamics – states that when heat Q is added to a system while the system does work W, the internal energy U changes by an amount equal to Q – W; ΔU = Q – W
· State – defined as the physical condition of the system
· 2nd Law of Thermodynamics – describes the directionality of natural thermodynamic processes
· 2nd Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius’ Statement) – heat can flow spontaneously from a hot object to a cold object; heat will not flow spontaneously from a cold object to a hot object
· 2nd Law of Thermodynamics (Engine Statement) – no cyclic process can convert heat completely into work
· 2nd Law of Thermodynamics (Refrigerator Statement) – no cyclic process can transfer heat from a colder place to a hotter place with no input of mechanical work
· Heat Engine – any device that changes thermal energy into mechanical work
· Entropy – a quantitative measure of the degree of disorder or randomness of a system
· Irreversible Process – all thermodynamic processes that occur in nature; processes that proceed spontaneously in one direction but not the other
· Reversible Process – a process where the system is always in thermodynamic equilibrium; an idealization that can never be precisely attained in real world
· Efficiency of an engine – defined as the ratio of the work (W) it does to the heat input at the high temperature
· Carnot Engine – an idealized engine
·  Efficiency of Carnot Engine – the heat Q1 (or QH) and Q2 (or QL) are proportional to the operating temperatures T1 (TH) and T2 (TL) in Kelvins
Efficiency of Carnot Engine – the heat Q1 (or QH) and Q2 (or QL) are proportional to the operating temperatures T1 (TH) and T2 (TL) in Kelvins
· Luminous Object – object that give off light
· Non-luminous object – object that do not give-off light
· Reflection – bouncing of light rays from a reflecting surface or mirror
· 1st Law of Reflection – the incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface all lie in the same plane
· 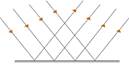
 2nd Law of Reflection – the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
2nd Law of Reflection – the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
· Regular Reflection – reflection that occurs in a smooth surface
· Irregular Reflection – reflection that occurs in a rough surface
· Virtual Image – an image formed by light rays that do not converge at the location of the image
· Real Image – an image formed by light rays that converge at the location of the image
· Concave Mirror – spherical mirror shaped like the inside of a bowl
· Convex Mirror – spherical mirror shaped like the outside of a bowl
· Principal Axis of a Spherical Mirror – a line that goes through the center of curvature to the center of the mirror
· Focal Length of a Spherical Mirror – distance from the principle focus to the center of the mirror; it is equal to one half of the radius of curvature of mirror
· Center of Curvature – the distance from the center of the mirror is equal to the radius of curvature of a mirror
· Object Distance – distance of the object (point 0) from the center of the mirror
· Image Distance – distance of the image (point I) from the center of the mirror
· Image Magnification – defined as the height of the image divided by the height of the object
· Index of Refraction – the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum (c) to the speed (v) in a given material medium
· Refraction – bending of light rays as it enters transparent material medium
· Snell’s Law – n1sinα = n2sinβ (α is angle of incidence and β is angle of refraction)
· Huygen’s Principle – all points in a given wave front are taken as point sources for the production of spherical secondary wavelets which propagate in space
· Lens – is a piece of clear plastic or glass with curved surfaces; it is usually circular, and its two faces are portion of a sphere
· Converging Lens – any lens that is thicker in the center than at the edges will make the parallel converge to a point
· Diverging Lens – lens that are thinner in the center than at the edges
· Principal Axis of a Lens – straight line passing through the center of the lens and perpendicular to its two surfaces
· Focal Point of a Lens - point where parallel rays meet after passing through the lens
· Focal Length of a Lens – distance of the focal point from the center of the lens
· Power of Lens – reciprocal of the focal length
· Diopter – unit for the power of lens
· Lens Aberration – distortion in an image; a distortion in an image produced by a lens or mirror, caused by limitations inherent to some degree in all optical systems
· Spherical Aberration – a distortion of an image caused by some light rays that pass through the edges of a lens focusing at a slightly different place from where light passing near the center of the lens focuses
· Chromatic Aberration – is a distortion of an image caused when light of different colors (and thus different speeds and refractions) focuses at different points when passing through a lens
Дата добавления: 2015-10-31; просмотров: 157 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| FOR- free on rail | | | TELEVISION IN BRITAIN |