
|
Читайте также: |
2.1. Place 3-5 drops of 0,5N manganese (ІІ) sulfate solution into each of three test tubes and add to each one 3-4 drops of 2 M sodium hydroxide solution until precipitate forms. After that stir the precipitate into the first test tube with glass rod and leave it in a stand for some time. Add 2-4 drops of 2M hydrochloric acid solution to the second test tube, and the same amount of 2 M sodium hydroxide solution into the third one. What can you observe? How and why did the colour of the precipitate in the first test tube change? Give the equations of the relevant reactions.
2.2. Add 3-4 drops of 0,5N manganese (ІІ) sulfate solution to the test tube with a neutral litmus solution. What can you observe? Write down the equation of the hydrolysis.
2.3. Place 3-4 drops of 0,5 M ammonium persulfate solution, 1 droplet of 2N sulfuric acid solution, 2 drops of silver nitrate solution into a test tube, heat up the mixture, and then add to it by glass rod a droplet (as small as possible, because, if the concentration of Mn2+ ions is too great, the precipitate Mn(OH)2 is formed instead of ions MnО 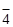 ) of 0,5N manganese (ІІ) sulfate solution. What can you observe? Why did the colour of the solution in the test tube change? What role do silver ions play? Give the equation of the reaction.
) of 0,5N manganese (ІІ) sulfate solution. What can you observe? Why did the colour of the solution in the test tube change? What role do silver ions play? Give the equation of the reaction.
2.4. Place 1-2 mls of 0,5N manganese (ІІ) sulfate solution into a test tube, add 2-3 drops of 1М sodium hydroxide solution and 3-4 drops of hydrogen peroxide solution with the weight fraction of H2О2, equal to 10%. Heat the mixture until the evolving of oxygen terminates, owing to complete decomposition of excess amount of hydrogen peroxide. What can you observe? Give the equation of the reaction.
2.5. Put few crystals of manganese (IV) oxide into a test tube and add 4-5 drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid. What can you observe? What properties does manganese (IV) oxide show? Give the equation of the reaction.
2.6. Heat up crystals of potassium permanganate in a test tube. The cooled heels transfer to a beaker containing 50 mls of water. What substance stipulates colour of a solution and why is it changed fastly? Give the equations of the relevant reactions.
2.7. Heat up crystals of potassium permanganate in a test tube. Transfer the cooled heels to a beaker containing 50 mls of diluted sodium hydroxide solution. What substance causes the colour of the solution? Add chlorine water to this solution. What can you observe? Give the equations of the relevant reactions.
2.8. Place 3-5 drops of 0,5N potassium permanganate solution into a test tube and add the same amount of 0,5N manganese (ІІ) sulfate solution. What can you observe? Immerse blue litmus paper in the test tube. How did the colour change? Give the equation of the reaction.
2.9. Place 3-5 drops of 0,5N potassium permanganate solution into each of three test tubes and add 2-4 drops: of 1 M sulfuric acid solution into the first, of water into the second, of 2 M sodium hydroxide solution into the third. Put 2-3 microspatulas of crystalline sodium sulfite into each test tubes. How does the solution change colour in each test tube? Give the equations of the reactions.
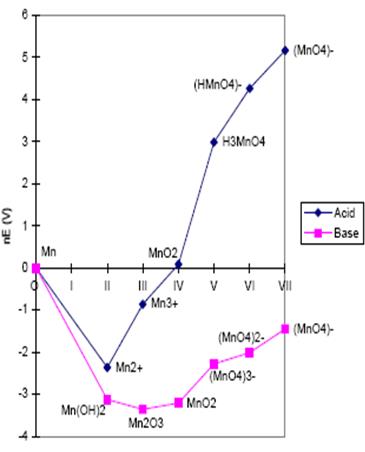 Frost diagram for manganese
Frost diagram for manganese
If the line has a postitive slope, the higher-lying species is an oxidizing agent. If the line has a negative slope, the higher-lying species is a reducing agent.
Thus for Mn in both acid and base solution, MnO4– is an oxidizing agent (the line has a positive slope), being reduced to several possible manganese species of lower oxidation state.
Elemental manganese, (i.e. manganese metal) is a reducing agent (the line has a negative slope), being itself oxidized most readily to Mn2+ in acid solution, and Mn2O3
If a species lies above the line connecting its neighbors, it is thermodynamically unstable towards disproportionation. This has been described as a point lying along a concave line. For example, in basic solution MnO4 3– lies on a point which is above the line connecting MnO42– and MnO2. This means that the reaction:
2 MnO43– + 2H2O =MnO42– + MnO2 + 4OH–
is predicted to be product-favored
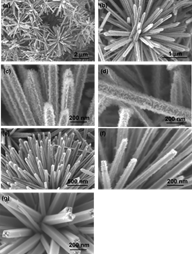
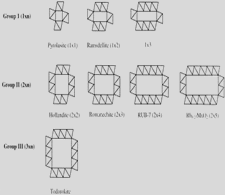
Morphology of crystallites and tunneled polymorphs of MnO2
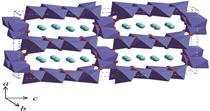
Graphical representation
Graphical representations of members of tunneled structure polymorphs of MnO2 and their diffractograms calculated with Powder Cell for Windows v. 2.4
Mendeleev's predicted elements
 To give provisional names to these predicted elements, Mendeleev used the prefixes eka-, dvi -, and tri-, from the Sanskrit words for one, two, and three, depending upon whether the predicted element was one, two, or three places away from the known element in his table with similar chemical properties.
To give provisional names to these predicted elements, Mendeleev used the prefixes eka-, dvi -, and tri-, from the Sanskrit words for one, two, and three, depending upon whether the predicted element was one, two, or three places away from the known element in his table with similar chemical properties.
Water oxidation:
The oxidation of water to form molecular oxygen lies at the heart of photosynthesis. The active site of the oxygen evolving complex (OEC) is known to contain a cluster of four manganese ions. Numerous attempts have been made to synthesise compounds capable of performing similar chemistry.
Дата добавления: 2015-07-25; просмотров: 87 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Make up the equations o f the reactions | | | Актуальные проблемы современного изучения истории русской литературы конца 1920- начала 1950-х годов. 1 страница |