
|
Читайте также: |
Four-stroke engines are usually medium speed or high-speed engines.
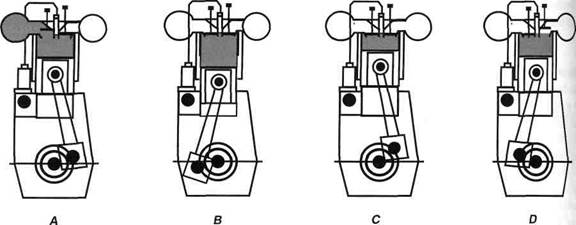
The four-stroke cycle begins when the piston is in its Top Dead Centre (TDC).
During the inlet stroke (also called suction stroke or air-induction stroke) the inlet valve is opened and air is drawn into the cylinder (A).
During the compression stroke, when the piston has just passed its Bottom Dead Centre (BDC), the inlet valve is closed and the air in the cylinder is compressed by the piston going up (B).
At the end of this stroke the fuel is injected by the atomizer. The nozzle on the atomizer divides the fuel into very small particles, so that it can mix with the air in the cylinder.
During the power stroke the mixture of air and fuel is burnt by the high temperature in the cylinder The "explosion" that follows will move the piston down (C). The reciprocating piston and connecting rod will cause the crankshaft to start rotating, which will actuate the camshaft. Now the rocking lever will actuate the valve mechanism.
In the four-stroke cycle the exhaust gases in the cylinder are removed by the piston itself. During this exhaust stroke the exhaust valve is opened, allowing the exhaust gases to escape from the cylinder (D).
|
Дата добавления: 2015-07-25; просмотров: 114 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Part V. The working of a two-stroke engine | | | Part VII. The valve mechanism |