
Читайте также:
|
Laws of thermal radiation allow to use as a characteristic of not blackbody so-called black temperature as well as emissivity.
Black temperature is such a conditional value blackbody must have so that its radiation is equal to that of real body. Every body can be characterized by a range of black temperatures depending on kind of radiation.
When comparing total integral radiation fluxes emitted by body having temperature Т and blackbody black temperature is called radiational (Т r). As follows from definition

or according to Stefan-Boltzmann law


If black temperature is determined on comparison of given body color with that of blackbody it is called color temperature (Т c). In this case monochromatic radiation for some two wave-length (colors) is usually considered.
According to definition following expression is considered
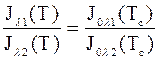 . (а)
. (а)
Using e l1 and e l2 in Wien’s law we get
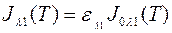 . (b)
. (b)
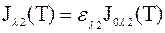 . (c)
. (c)
Substituting expressions (b) and (c) into equation (a) we get
 . (d)
. (d)
Substituting expressions for Plank’s law instead of radiation intensity we get
 .
.
After transformations we get

or  .
.
Taking the logarithm from this expression we obtain
 ;
;
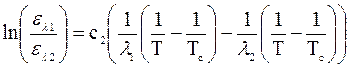 ;
;
 .
.
So finally we get
 .
.
If intensity of given body monochromatic radiation is compared with that of blackbody then black temperature is called brightness temperature (Т b). As follows from definition
 .
.
Substituting  and using Wien’s law we get relationship between Т and Т b.
and using Wien’s law we get relationship between Т and Т b.
Brightness of monochromatic radiation is
 ,
,
where  .
.
Then we get
 ,
,
where from  .
.
Taking the logarithm we get

or
 .
.
Дата добавления: 2015-08-17; просмотров: 42 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| This dependence is called square of distances law | | | Выбор степени подвижности бетонной смеси |