Transcription
Theme 6
Genes. Structure and function of genes.
1. Learn Basic Anatomy of a Gene
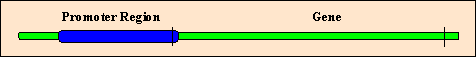
- Promoter - Region of DNA where RNA polymerase attaches and initiates transcription
- Gene - area of DNA which codes mRNA
Transcription
- RNA polymerase binds to promoter region and pries the two strands of DNA apart
- RNA polymerase can only bind to one of the strands of DNA at the 3' end (so that the transcribed mRNA will be constructed 5' to 3')
- The stretch of DNA that will be transcribed is known as the transcription unit
- The promoter includes the transcription start point (AUG) and typically extends several dozen bases "upstream"
- RNA polymerase binds to DNA and begins to synthesize mRNA
- In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase specifically recognizes the promoter and binds
- In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase binding is mediated by one or many proteins called transcription factors
- These transcription factors must be completely bound to the promoter in order for RNA polymerase to bind
- The TATA box is a region about 25 bp's up from the start point which is recognized by the transcription factors
- The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase bound to the promoter is known as the transcription initiation complex
- When RNA polymerase is finished, mRNA leaves and is either modified or immediately used to form protein
- Transcription in prokaryotes terminates immediately after the stop sequence is transcribed
- In eukaryotes, transcription usually proceeds at least 30 bp's after the RNA stop signal.
- There is usually a AAUAAA sequence transcribed in the mRNA (TTATTT on the DNA).
- Termination of transcription occurs shortly thereafter
2. Learn the Genetic Code
- universal - with very few exceptions, all organisms use the same code in the formation of protein
- mRNA bases read as triplets (codons). The codons are non-overlapping
- The genetic code is redundant (64 combinations, only 20 aa's)
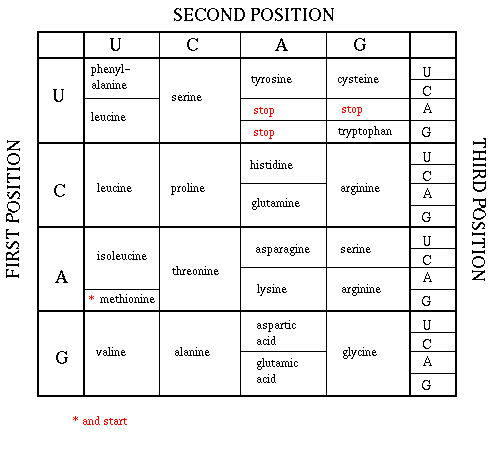
o Example: CCC, CCU, CCA, CCG all code for Proline
3.Write the corresponding amino acids
| AUG
| UAU
| CAU
| UAC
| GGA
| UAA
| AUG
| CCU
| UAA
| UAU
| UAA
|
|
|
| o
| o
| o
| o
| o
| o
| o
| o
| o
|
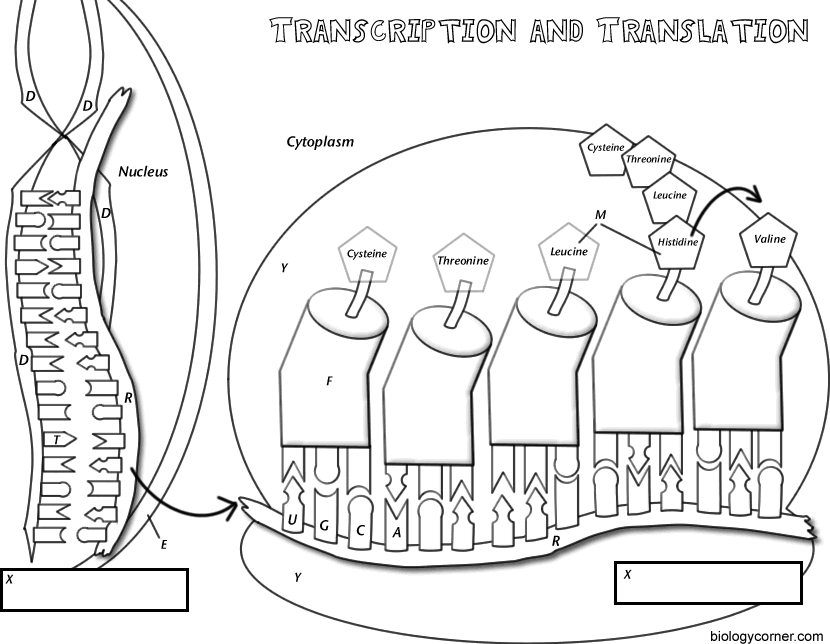
4. Learn the structure of tRNA and draw a diagram of the structure of tRNA
|
| tRNA is the interpreter of the codons contained in a mRNA
- The function of tRNA is to transfer amino acids from teh cytoplasm's amino acid pool to a ribosome
- The Cell keeps its cytoplasm well stocked with all 20 amino acids, either by synthesizing them or by taking them up from the surrounding solution
- A charged tRNA is one which has a specific amino acid bound to the acceptor arm
- Each tRNA has a three-base sequence called the anticodon which binds to a complementary triplet on the mRNA according to the base-pairign rules
|
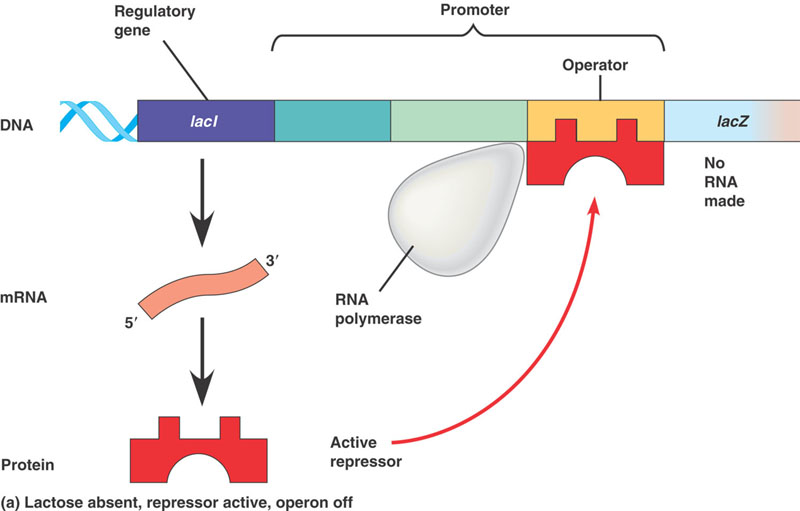
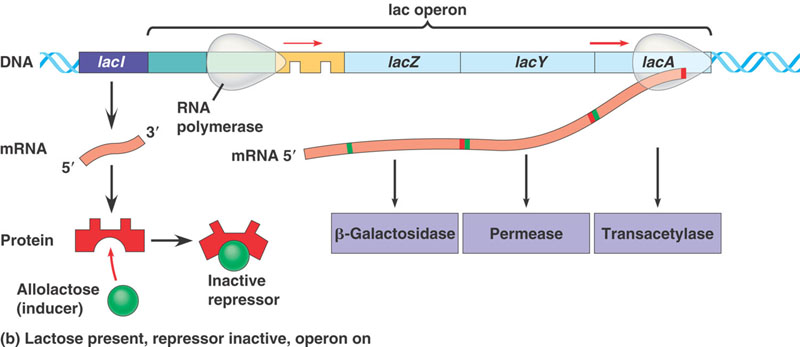
5. Learn Lac operon - set of inducible genes involved in digestion of lactose.
Дата добавления: 2015-08-10; просмотров: 55 | Нарушение авторских прав
mybiblioteka.su - 2015-2025 год. (0.01 сек.)





