
Figure20. EM of a human mature monocyte; C, centriole; G, Golgi apparatus; L, lysosomes; M, mitochondria
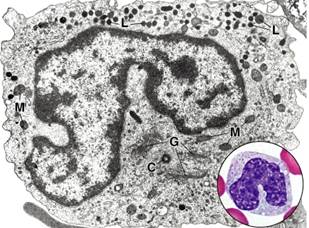
Monocytes are bone marrow derived agranulocytes. They are large and constitute only 3 to 11% of the white blood cells. The nucleus is oval, horseshoe- or kidney-shaped. The cytoplasm of the monocyte is basophilic and frequently contains very fine azurophilic granules (lysosomes). The monocytes contain well developed Golgi apparatus, centrioles, sER and rER and small mitochondria. Blood monocytes are precursor cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system. After crossing capillary walls and entering connective tissues, monocytes differentiate into macrophages.
Main functions are:
-monocytes are highly phagocytic cells, but not in the blood stream.
-they leave vessels and go the connective tissue, transform there into macrophages and take place in the phagocytosis of bacteria.
Дата добавления: 2015-07-25; просмотров: 53 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Lymphocytes | | | Platelets |