
Real and Nominal GDP
| video games | energy drinks | |
| year 1 price | ||
| year 1 output | ||
| year 2 price | 2.5 | |
| year 2 output | ||
| year 3 price | 2.5 | |
| year 3 output |
130. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year one is the base year, then the real GDP in year two, is ________.
A) 5000
B) 5250
C) 5900
D) 6175
E) none of the above
131. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year one is the base year, then the real GDP in year three, is ________.
A) 7200
B) 8250
C) 1050
D) 7500
E) none of the above
132. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year one is the base year, then the nominal GDP in year two, is ________.
A) 8250
B) 5000
C) 7200
D) 7500
E) none of the above
133. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year three is the base year, then the real GDP in year two is ________.
A) 8250
B) 5900
C) 7500
D) 6775
E) none of the above
134. The inflation rate = ________.
A) nominal GDP - real GDP
B) growth rate in real GDP — growth rate in nominal GDP
C) growth rate in real GDP + growth rate in nominal GDP
D) nominal GDP ÷ real GDP
E) none of the above
Real and Nominal GDP
| video games | energy drinks | |
| year 1 price | ||
| year 1 output | ||
| year 2 price | 2.5 | |
| year 2 output | ||
| year 3 price | 2.5 | |
| year 3 output |
135. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year one is the base year, then the GDP deflator for year two is ________.
A) 95.5
B) 123.5
C) 118
D) 104.7
E) 116.6
136. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year one is the base year, then the GDP deflator for year three is ________.
A) 165
B) 139.8
C) 85.8
D) 133.6
E) 114.6
137. Based on the table "Real and Nominal GDP," if year one is the base year, then the inflation rate in year three is ________.
A) 14.6%
B) 9.5%
C) 9.9%
D) 11.5%
E) 16.5%
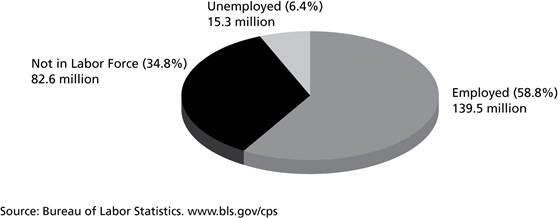
138. According to Figure above, the United States labor force in April 2010 was ________.
A) 154.8 million
B) 139.5 million
C) 237.4 million
D) 222.1 million
E) none of the above
139. According to Figure above, the United States unemployment rate in April 2010 was ________.
A) 6.4%
B) 18.5%
C) 9.9%
D) 65.2%
E) none of the above
140. According to Figure above, the United States labor force participation rate in April 2010 was ________.
A) 6.4%
B) 18.5%
C) 9.9%
D) 65.2%
E) none of the above
141. According to Figure above, the United States civilian employment ratio in April 2010 was ________.
A) 142.5%
B) 34.8%
C) 58.8%
D) 65.2%
E) none of the above
142. A discouraged worker might ________.
A) be counted as unemployed
B) have tried to find a job during the month prior to the household survey, but without success
C) have been prevented from working during the week prior to the household survey, due to illness or other temporary circumstances
D) be waiting to return to a job from which he or she has been laid off
E) none of the above
143. The nominal interest rate ________.
A) makes no allowance for inflation
B) is a percentage of the amount borrowed
C) is the rate that most banks advertise
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
144. The Fisher equation implies ________.
A) the nominal interest rate equals the real rate of inflation plus expected inflation
B) the real interest rate equals expected inflation
C) expected inflation equals current inflation
D) the growth rate of inflation equals the real minus the nominal rates of interest
E) none of the above
145. The Fisher equation implies that an increase in the nominal rate of interest relative to the real rate indicates that ________.
A) inflation is expected to rise
B) inflation is expected to decrease
C) the real cost of borrowing has increased
D) the real cost of borrowing has decreased
E) none of the above
146. Increases in ________ typically lead to decreases in consumption
A) the interest rate
B) disposable income
C) autonomous consumption
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
147. ________ typically lead to increases in ________.
A) decreases in interest rates; investment
B) increases in disposable income; consumption
C) increases in autonomous investment; investment
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
148. In the long run, if government increases spending ________.
A) interest rates decrease
B) it crowds out private investment
C) saving increases
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
149. In the long run, larger budget deficits lead to ________.
A) higher saving levels
B) a fall in investment
C) lower interest rates
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
150. In an open economy, Y = C + I + G + NX. From this we may infer that ________.
A) output is greater in an open economy than in a closed economy
B) the condition for goods market equilibrium is that S = I + G + NX
C) net exports can be zero only if the domestic real interest rate is equal to the world real interest rate
D) if saving is greater than zero, NX cannot be zero
E) none of the above
151. Fred has always been known as "the rich kid." Strictly speaking, this must mean that ________.
A) Fred has a lot of cash
B) Fred's income is quite high
C) Fred won the lottery before he was legally eligible
D) Fred has a flashy wardrobe
E) Fred has a lot of wealth
152. In modern economies, the supply of money depends mainly on the economy's ________.
A) tax rates
B) mining of precious metals
C) net exports
D) growth of output of goods and services
E) none of the above
153. Open Market operations consist mainly of ________.
A) the government buying and selling private securities in the open market
B) the NB buying and selling government securities in the open market
C) the government selling its own securities in the open market
D) the NB setting rates for securities traded in the open market
E) none of the above
154. When the NB sells government securities in the open market, the money supply ________ because ________.
A) decreases; banks lose liquidity, they make fewer loans and checking account deposits decrease
B) increases; banks gain liquidity, they make more loans and checking account deposits increase
C) increases; banks lose liquidity, they make more loans and checking account deposits increase
D) decreases; banks gain liquidity, they make fewer loans and checking account deposits decrease
E) none of the above
155. When the NB buys government securities in the open market, the money supply ________ because ________.
A) decreases; banks lose liquidity, they make fewer loans and checking account deposits decrease
B) increases; banks gain liquidity, they make more loans and checking account deposits increase
C) increases; banks lose liquidity, they make more loans and checking account deposits increase
D) decreases; banks gain liquidity, they make fewer loans and checking account deposits decrease
E) none of the above
156. The NB's narrowest measure of money is ________.
A) M1
B) M2
C) M3
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
157. M1 does not include cash that is held in ATMs or bank vaults, because ________.
A) no one really owns that money
B) that money is included in M2
C) that money earns no interest
D) the right to access that money is counted already as bank deposits
E) none of the above
158. Which of these transactions results in an increase in M2?
A) certificate of deposit matures, adding $520 to your checking account
B) withdrawal of $100 cash from your checking account
C) depositing a bank loan of $400 into your savings account
D) depositing a $300 paycheck into your savings account
E) none of the above
159. If the euro replaces the U.S. dollar as the world's most popular currency, that will likely ________.
A) reduce M1, without affecting M2
B) reduce M2, without affecting M1
C) cause a temporary increase in M1
D) affect neither M1 nor M2
E) none of the above
160. As of 2010 the outstanding U.S. currency is $872 billion, which implies that the typical U.S. citizen holds $2,800 in cash. Is this an accurate inference? Why?
A) Yes; because dividing total currency of $872 billion by total U.S. population in 2010 roughly works out to $2,800 per person
B) No; because criminals and foreigners hold large sums of dollars, so the average citizen holds far less.
C) No; because the average citizen probably does not have $2800 in her checking account to back up all that cash
D) Yes; because the Fed rarely makes accounting mistakes when computing M1
E) none of the above
161. The quantity theory of money explains how ________ depends on ________.
A) real GDP; the money supply
B) the price level; the demand for money
C) the money supply; the velocity of money
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
162. The quantity theory of money tells us that real money balances are proportional to income, since ________.
A) velocity is assumed constant in the short run
B) the supply and demand of money are equal in equilibrium
C) changes in the quantity of money lead to proportional changes in the price level
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
163. From the equation of exchange, if both nominal income and the quantity of money (M) double, the price level (P) decreases by 50 percent and velocity (V) remains constant, then real output (Y)________.
A) also doubles
B) triples
C) quadruples
D) decreases by 50 percent
E) none of the above
164. From the equation of quantity theory of money, if both real income (Y) and the quantity of money (M) double and the price level (P) remains constant, then velocity (V)________ and nominal income ________.
A) remains constant; doubles
B) doubles; remains constant
C) doubles; doubles
D) decreases by 50 percent; quadruples
E) none of the above
165. Suppose Y = 100, P = 80, and V = 3.2. If Y rises to 105, and the inflation rate is 10 percent, what is the new value of M?
a) 29568.5
B) 9240.5
C) 2500.0
D) 2,887.5
166. Productivity growth can be measured ________.
A) by dividing output by Kt0.3 Lt0.7
B) by adding the contributions from capital growth and labor growth
C) by subtracting the contributions from capital growth and labor growth from the growth of output
D) by dividing the growth of output by the contributions from capital growth and labor growth
167. Productivity is ________.
A) determined by central bank policy
B) the combined effect of monetary and fiscal policy
C) the residual component of the production function
D) driven by changes in the rate of growth of output
168. If productivity growth equals 3.0 percent, the contribution from capital growth 1.2 percent and the contribution from labor growth 2.0 percent, then output growth must equal ________.
A) 2.2 percent.
B) 4.2 percent.
C) 6.2 percent.
D) 7.2 percent.
169. If the contribution from capital and labor growth in a given economy equals 4.0 percent and output growth equals 6.4 percent over that same period of time, then productivity growth must equal ________.
A) 25.6 percent.
B) 10.4 percent.
C) 2.4 percent.
D) 1.6 percent.
170. The growth rate of which of the following is not a component of the growth accounting equation?
A) the capital stock.
B) labor.
C) depreciation.
D) available technology.
171. If the contribution from capital growth equals 3 percent and the contribution from productivity growth equals 1.6 percent, GDP will grow by ________.
A) 1.6 percent.
B) 4.6 percent.
C) 4.8 percent.
D) an unknown value.
172. If the contribution from capital growth equals 2 percent and the contribution from labor growth equals 4 percent, then GDP ________.
A) will grow by 6 percent.
B) will grow by 8 percent.
C) will grow by 2 percent.
D) will change by an unknown percentage
173. Given the production function Y = A K0.3L0.7if output grows by five percent, the capital input grows by five percent, and the labor input grows by two percent, calculate the technology change rate. Calculate the growth rates of output per worker.
A) 0.021; 0.03
B) 0.02; 0.05
C) 0.3; 0.21
D) 0.021; 0.05
174. In a closed economy ________.
A) investment equals consumption.
B) investment equals savings.
C) saving equals consumption.
D) exports are greater than imports.
175. In the bathtub analogy, which of the following is a stock variable?
A) the amount of investment.
B) the rate of depreciation.
C) the amount of capital-per worker.
D) the Cobb-Douglass value.
176. If an economy invests more than it loses through depreciation ________.
A) the saving rate will fall.
B) the saving rate will rise
C) the quantity of labor will fall.
D) the capital stock will expand.
177. The loss of capital due to the wearing out of machines is known as ________.
A) saving.
B) investment.
C) consumption.
D) depreciation.
178. A higher rate of saving at the national level will, in the long-run ________.
A) cause a decrease in levels of capital and output.
B) have no effect on levels of capital and output.
C) lead to an increase in population growth.
D) cause an increase in levels of capital and output.
179. In a steady-state economy with no population growth, output per worker is 35, the saving rate is 20 percent, and the depreciation rate is 11 percent. The level of capital per worker is ________.
A) 318.2
B) 256.4
C) 168.3
D) 280.5
180. In a steady-state economy with no population growth, consumption per worker is 45, the saving rate is 25 percent, and the depreciation rate is 15 percent. The level of capital per worker is ________.
A) 4
B) 400
C) 40
D) 4000
181. Other things the same, in the Solow model in the steady state, a higher rate of population growth ________ the level of output per worker.
A) leads to an increase in
B) has no long-run effect on
C) has an ambiguous effect on
D) leads to a decrease in
182. If output per worker in a steady state is $30,000, depreciation is 13%, the population growth rate is two percent, and the saving rate is 20%, what is the steady state capital-labor ratio (k)?
A) 145600.5
B) 150727.3
C) 140868.5
D) 130434.7
183. On the Solow Diagram, an increase in population growth is shown by
A) an upward shift of the depreciation plus capital line
B) an upward shift of the investment function
C) an upward shift of the per-worker production function
D) a downward shift of the investment function
184. A One-Child Policy was instituted in 1979 in ________.
A) Brazil.
B) South Africa.
C) India.
D) China
185. Total planned expenditure (equals total output) is 14,000 when autonomous consumption expenditure is 450. When autonomous consumption expenditure falls to 400, total planned expenditure (equals total output) is 13,800. The marginal propensity to consume is ________.
A) 0.89
B) 0.75
C) 0.99
D) 0.44
E) 0.03
186. Total planned expenditure (equals income) is 13,500, autonomous consumption expenditure is 600, the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, government purchases are 2,700, taxes are 2,500 and planned investment spending is ________.
A) 1750
B) 1400
C) 1200
D) 1800
187. An increase in the real interest rate will cause an increase in ________.
A) saving
B) planned investment
C) net exports
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
188. The IS curve ________.
A) shows the relationship between aggregate output and the real interest rate when the goods market is in equilibrium
B) tells us that increases in autonomous consumption, investment, government purchases raise output for any real interest rate
C) tells us that a decrease in taxes leads to increases in output for any given real interest rate
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
189. In the IS curve ________.
A) an increase in the interest rate constitutes an upward movement along the curve
B) an increase in aggregate consumption constitutes a downward movement along the curve
C) an increase in taxes constitutes a rightward shift of the curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
190. The relative price of one currency in terms of another is known as the ________.
A) nominal exchange rate.
B) real exchange rate.
C) domestic price level.
D) real interest rate.
191. The relative price of goods in two countries is known as the ________.
A) nominal exchange rate.
B) real exchange rate.
C) domestic price level.
D) real interest rate
192. An increase in the value of a country's currency is known as ________.
A) a spot exchange rate.
B) a depreciation of its value.
C) an appreciation of its value.
D) a backward exchange rate.
193. Suppose that a haircut in your hometown costs $20, while the price for the same haircut in Mumbai is 600 Indian rupees. At which nominal exchange rate is the dollar price lower for the Mumbai haircut?
A) 0.029$/Rs.
B) 20Rs./$
C) 25Rs./$
D) 0.04$/Rs.
194. Suppose that a haircut in your hometown costs $20, while the price for the same haircut in Mumbai is 600 Indian rupees. At which nominal exchange rate is the dollar price lower for the Mumbai haircut?
A) 0.029$/Rs.
B) 20Rs./$
C) 25Rs./$
D) 0.04$/Rs.
195. Suppose you reserve a hotel room in Madrid for $300 per night. When you check out, you are charged only $285 per night. Assuming that the price of the room in euros had not changed, and that the nominal exchange rate had been 0.8 (euros/$) when the reservation was made, the new nominal exchange rate is ________.
A) 0.84
B) 0.76
C) 0.95
D) 1.05
196. Suppose an item sells for $125 in the United States and for 62,500 pesos in Chile. According to the law of one price, the nominal exchange rate (pesos/dollar) should be ________.
A) 31,313
B) either $125, or 62,500 pesos, but not both
C) 0.002
D) 500
197. Suppose the nominal exchange rate rises from 82 to 90. The domestic currency has appreciated by ________ percent.
A) ten
B) nine
C) eight
D) 86
198. In a fixed exchange rate regime, the value of a currency is pegged to ________.
A) an anchor currency.
B) a currency board.
C) a dirty float.
D) an interest rate standard such as the Treasury bill rate in the U.S.
199. Suppose total government spending is increased permanently by ten percent, with no change in tax rates. In the long run, the resulting deficit will disappear, ________.
A) only if government spending is brought back down to the original level
B) if economic growth raises tax revenue by ten percent
C) if the government debt is sold to foreigners
D) unless the money is spent entirely on government consumption
200. Fiscal policy involves manipulating ________.
A) the supply of money.
B) consumption spending.
C) federal subsidies and minimum wage values.
D) government spending and taxes.
Дата добавления: 2015-07-25; просмотров: 521 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Премьер – Экспресс | | | по ремонту и техническому обслуживанию автомобилей |