
|
Читайте также: |
Climate is often defined as average WEATHER, when weather means the current state of the atmosphere. For scientists, climates are the result of exchanges of heat and moisture at the Earth's surface. Because of its size, Canada has many different climates. For example, there are drastic differences in day length from south to north: in December, southern Canada receives eight hours of daylight, while northern regions receive none. An area’s position on the continent, especially its distance from OCEANS, also affects climate. In Canada, this explains why a coastal city in British Columbia, such as VICTORIA, has a warmer climate than an interior city such as WINNIPEG, Manitoba.
Temperature
Temperature is the degree of warmness or coldness. Air temperatures have been measured in some places in southern Canada for over 100 years, but in the Arctic for a much shorter time. Climate statistics are usually expressed as 30-year averages published every 10 years.
In winter, when northern Canada receives very little sun, temperature differences from north to south are great. The mean maximum January temperature of ALERT, at the northern tip of ELLESMERE ISLAND, is -28.6°C, while in WINDSOR, ON, it is -0.4°C. That is a difference of 28.2°C. In the summer, the long days in northern Canada result in smaller north-south differences, with maximum temperatures in July of 6.1°C for Alert and 29°C for Windsor. That is a difference of 22.9°C.
In addition to monthly temperatures, climatologists also like to know the total amount of heat received by any given place. To express this total, climatologists have formulated an index of potential evapotranspiration (PE), derived from monthly temperatures above 0°C. Potential evapotranspiration is the amount of water that potentially would evaporate and transpire from a vegetated surface. Therefore, PE is an index of heat. The high arctic islands, for example, receive very little heat and have a PE of 200 mm. In comparison, the warmest areas in southern ONTARIO, QUÉBEC and BRITISH COLUMBIA have a PE approximately three times as high. Still, Canada’s maximum PE is but a fraction of that of tropical countries, where the PE exceeds 1,500 mm.
It is also important to note how cold a place can get, especially when considering the cost of heating homes. A parameter that summarizes coldness is the heating degree day (HDD). It is a calculation based on how far below 18°C (65°F) a day’s average temperature is, 18°C being the reference temperature below which heaters are typically turned on. Southern Ontario has 4,000 HDD annually, while the high arctic islands have 12,000 HDD.
Climate in Alberta
· 
· 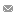
Alberta, as the fourth largest province in Canada, has a land area of 661,185 square kilometers. It is located between 45°N to 65°N and 105°E to 125°E. The altitude varies from 170 meters (above sea level) in the Wood Buffalo National Park in the northeast to as high as 3,747 meters (above sea level) in the Rocky Mountains along the southwestern border. This variation, as well as the variation in sea surface temperature of the Pacific Ocean, has a pronounced influence on the diversity of the climate.
For example, in the south-east region of Alberta, annual precipitation has ranged from a high of 689 mm (1927) to 186 mm (2001), the driest year on record. The flow of the South Saskatchewan River reflects that variability. No place else in Canada, and few places on earth, have this much variability in both climate and annual water balance.
 Temperature
Temperature
Although most parts of Alberta could be classified as semi-arid, its climate varies considerably with daily mean temperatures in:
Precipitation
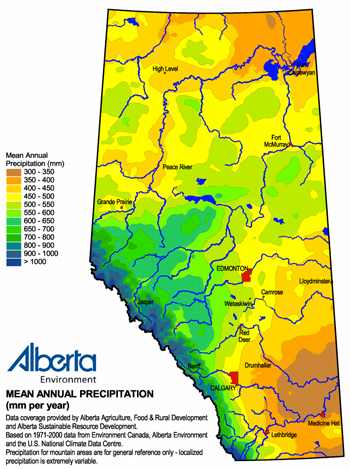
Annual precipitation ranges from 300 mm/year in the southeast to 450 mm/year in the north, except in the foothills of the Rocky Mountains where rainfall can reach 600 mm/year.
The average annual precipitation across teh province is 510 millimeters per year.
While precipitation in northern Alberta ranges from about 400 mm (northeast) to over 500 mm on the northwest, and precipitation in southern Alberta ranges from less than 350 mm (southeast) to about 450 mm.
The south and east-central portions are prone to drought-like conditions sometimes persisting for several years, although even these areas can receive heavy precipitation.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-16; просмотров: 160 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| California wants to lead America to a greener future | | | What is Climate? |