
Читайте также:
|
High Availability, Scalability, And Computing Power
3. What IaaS means and in which cases IaaS is most applicable? Give several examples.
In the most basic cloud-service model & according to the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force), providers of IaaS offer computers – physical or (more often) virtual machines – and other resources. (A hypervisor, such as Xen, Oracle VirtualBox, KVM, VMware ESX/ESXi, or Hyper-V runs the virtual machines as guests. Pools of hypervisors within the cloud operational support-system can support large numbers of virtual machines and the ability to scale services up and down according to customers' varying requirements.) IaaS clouds often offer additional resources such as a virtual-machine disk image library, raw block storage, and file or object storage, firewalls, load balancers, IP addresses, virtual local area networks (VLANs), and software bundles. IaaS-cloud providers supply these resources on-demand from their large pools installed in data centers. For wide-area connectivity, customers can use either the Internet or carrier clouds (dedicated virtual private networks). To deploy their applications, cloud users install operating-system images and their application software on the cloud infrastructure. In this model, the cloud user patches and maintains the operating systems and the application software. Cloud providers typically bill IaaS services on a utility computing basis: cost reflects the amount of resources allocated and consumed.
4. What PaaS means and in which cases it is most applicable? Give several examples.
In the PaaS models, cloud providers deliver a computing platform, typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. With some PaaS offers like Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine, the underlying computer and storage resources scale automatically to match application demand so that the cloud user does not have to allocate resources manually. The latter has also been proposed by an architecture aiming to facilitate real-time in cloud environments.
5. How to manage Azure Websites Service auto-scale and which metrics can be applicable for auto-scaling?
For increased performance and throughput for your web apps on Microsoft Azure, you can use the Azure Portal to scale your App Service plan from Free mode to Shared, Basic, Standard, or Premium mode.
Scaling up on Azure web apps involves two related actions: changing your App Service plan mode to a higher level of service, and configuring certain settings after you have switched to the higher level of service. Both topics are covered in this article. Higher service tiers like Standard and Premium modes offer greater robustness and flexibility in determining how your resources on Azure are used.
Changing modes and configuring them is easily done in the Scale tab of the management portal. You can scale up or down as required. These changes take only seconds to apply and affect all web apps in your App Service plan. They do not require your code to be changed or your applications to be redeployed.
Scaling to Shared or Basic mode
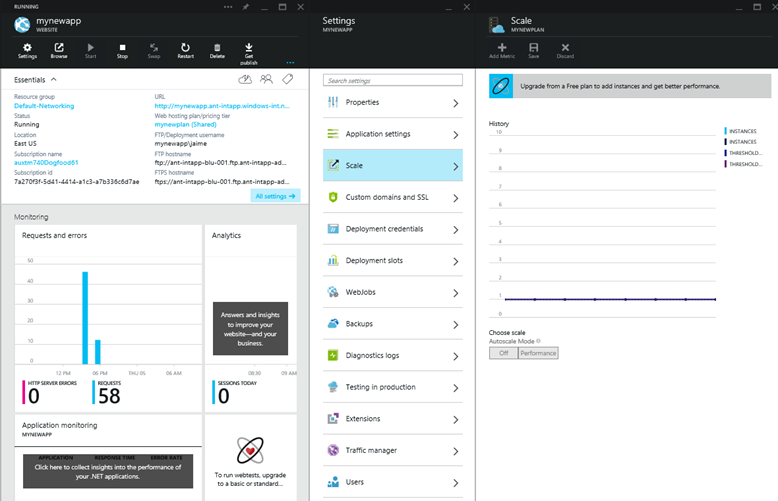
The Notifications tab will flash a green SUCCESS once the operation is complete.

The Notifications tab will flash a green SUCCESS once the operation is complete.
Scaling to Standard or Premium mode
The Notifications tab will flash a green SUCCESS once the operation is complete, and Autoscale Mode will be enabled.
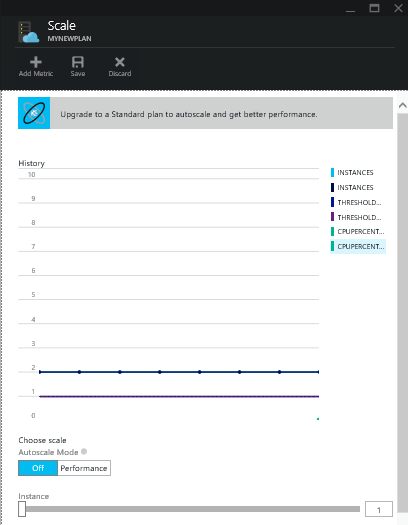
You can still slide the Instance bar to manually scale to more instances, just like in Basic mode as shown above. However, here you will learn how to use Autoscale Mode.


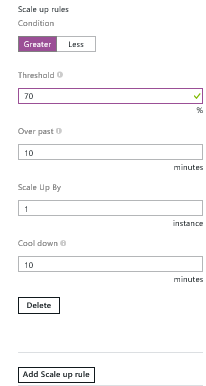
You can configure autoscaling rules for different performance metrics, including CPU, memory, disk queue, HTTP queue, and data flow. Here, you will configure autoscaling for CPU percentage that does the following:



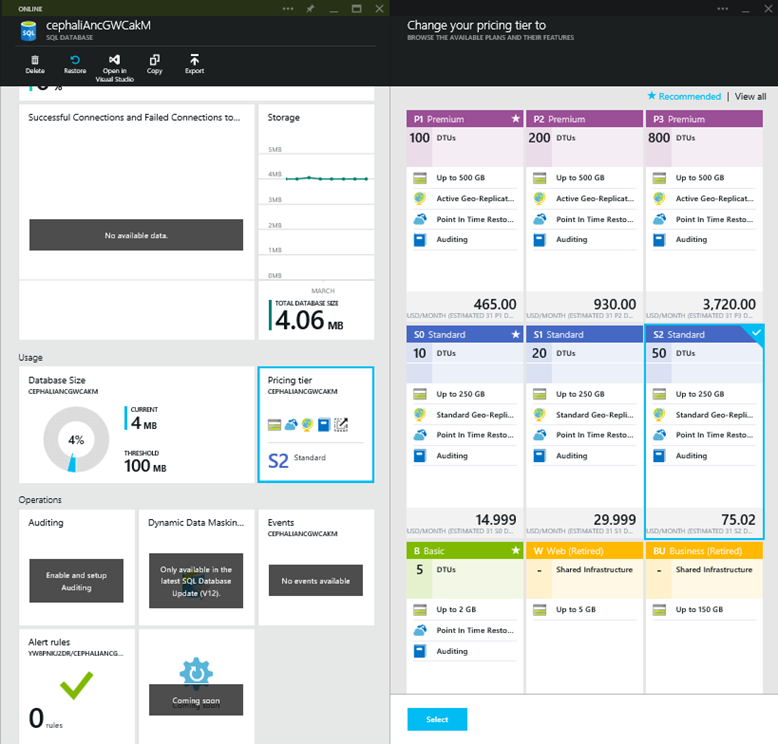
Scaling a SQL Server Database connected to your web app
If you have one or more SQL Server databases linked to your web app (regardless of App Service plan mode), you can quickly scale them based on your needs.

6. What can be backed up for Websites Service and how to manage it?
Website files, database (optional), Website settings manifest
7. Which Operating Systems can be used for Virtual Machines creating in Microsoft Azure, and what are maximum and minimum sizes of VMs allowed today (provide values)? Refer to:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/azure/dn197896.aspx
Дата добавления: 2015-10-24; просмотров: 127 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Explain project management with TFS | | | Service Bus provides a multi-tenant service for connecting applications through the cloud. |