
|
Читайте также: |
a string of prestige brand names
accounts, pay into bank account
acknowledgement
air waybill
assets
assign a credit limit
bank reference
bill
cash flow
credit control
deliver
delivery note
down payment
downturn
economic slowdown
face value
free trade area
freight
gross profit
handling charge
inconsistent
interest
annual rate of interest
interest charge
launch
ledger
marginal increase
merchandise
negotiate
net profit
operating income
operating profit
overall group sales
overdraw an account
overdue payment
overseas
owe
partshipment
purchase
quotation
rectify
remittance
retail
shipment
shipping
spreadsheet
stipulate
supplier
transhipment
VAT
Factoring (факторинг) is a financial transaction whereby a business job sells its accounts receivable (i.e., invoices) to a third party (called a factor) at a discount in exchange for immediate money with which to finance continued business. Factoring differs from a bank loan in three main ways. First, the emphasis is on the value of the receivables (essentially a financial asset), not the firm’s credit worthiness. Secondly, factoring is not a loan – it is the purchase of a financial asset (the receivable). Finally, a bank loan involves two parties whereas factoring involves three.
Port of discharge – the port at which cargo is unloaded
Bill of exchange ((переводный) вексель, тратта) – a document containing an instruction, usually to a bank, to pay a stated sum of money at a specified future date or on demand
Drawn at sight – a bill of exchange, payable when the beneficiary presents it at the bank, is said to be ‘drawn at sight’
Sight draft (вексель на предъявителя) is most commonly used in international trade. In a sight draft, the payment is on demand or on presentation of the negotiation documents to the paying bank or the importer. In practice, the bank may pay within three working days (not instantly) after the receipt and review of the negotiation documents and if they are in order, that is, the documents comply exactly to the letter of credit stipulations.
Incoterms ("ИНКОТЕРМС" - издание Международной торговой палаты) – a glossary of terms used in international commerce and trade, published by the International Chamber of Commerce. The most common ones are:
CIF (условие поставки «стоимость, страхование и фрахт») – the price covers Cost, Insurance and Freight to a named port of destination in the buyer’s country.
EXW (условие поставки «с завода») – the price is Ex-Works cost of the goods. The buyer arranges collection from the supplier and pays for the freight carriage and insurance.
FOB (условие поставки «свободно на борту») – the price includes all costs of the goods Free On Board a ship (or aircraft) whose destination is stated in the contract. The buyer pays for onward shipment and insurance.
Methods of payment in foreign trade:
CWO – cash with order (наличный расчет при выдаче товара). This method is uncommon since you extend credit to your supplier, in addition you run the risk that the goods will not be dispatched in accordance with the contract terms. But this is usual with mail order, where you pay by Eurocheque or cheque or by using a credit card. In business CWO contracts often include provision for partial advance payments in the form of deposits (normally between 10% – 20% of the contract price). Or they include progress payments at various stages of manufacture (particularly for capital goods). Then the remainder of the payment is usually made by one of the methods described below.
Open account (открытый счет). This is a simple agreement in which you agree to pay for the goods after you have received them, usually on a monthly basis. There are various ways in which you can send money to your suppliers under open account:
· Cheque
· Banker’s draft. You can arrange for your bank to issue a draft, which is a kind of cheque drawn on an overseas bank. You send this direct to your suppliers who pay it into their bank account. Then they will usually receive immediate credit.
· Telegraphic transfer (interbank transfer). Your bank instructs an overseas bank, by secure e-mail, to pay a stated amount of money to you suppliers.
· International payment order. You can arrange for your bank to instruct an overseas bank to make payment to you supplier, by airmail.
· International money orders. You post the money order to your suppliers and they receive immediate credit from their bank in the same way as with a draft.
Documentary Bill of Exchange ((переводный) вексель, тратта). The main advantage is that you are not required to make payment until your suppliers have dispatched the goods.
Vocabulary exercise: match the words with their definitions
assets
auditing
bookkeeping
cost accounting
expenditure
financial accounting
income
liabilities
management accounting
tax accounting
1. Anything owned by a company – cash, buildings, machines, etc.
2. Calculating how much tax an individual or a company should pay – or trying to reduce the figure.
3. Checking and evaluating financial records.
4. Determining the unit cost of a manufactured product, including indirect costs.
5. Keeping financial records and preparing financial statements.
6. Money that a company will have to pay for something else – bills, debits, interest, taxes, etc.
7. Recording transactions in ledgers.
8. The money that a company receives from supplying goods or services.
9. The money that a company spends.
10. The use of company’s accounting data by its managers for planning and control.
Letters of Credit
A letter from a bank guaranteeing that a buyer's payment to a seller will be received on time and for the correct amount. In the event that the buyer is unable to make payment on the purchase, the bank will be required to cover the full or remaining amount of the purchase. Letters of credit are often used in international transactions to ensure that payment will be received. Due to the nature of international dealings including factors such as distance, differing laws in each country and difficulty in knowing each party personally, the use of letters of credit has become a very important aspect of international trade. The bank also acts on behalf of the buyer (holder of letter of credit) by ensuring that the supplier will not be paid until the bank receives a confirmation that the goods have been shipped.
Irrevocable letter of credit – ILOC (безотзывный аккредитив) - a letter of credit that can't be canceled. This guarantees that a buyer's payment to a seller will be received on time and for the correct amount.
Revocable letter of credit (отзывной аккредитив) – a letter of credit which can be cancelled.
Invoice (счет, счет – фактура)is essentially a detailed bill left by vendors and outside suppliers for goods or services rendered to a company. A typical invoice lists:
· A unique reference number (in case of correspondence about the invoice)
· Date of the invoice.
· Tax payments if relevant (e.g. VAT)
· Name and contact details of the seller
· Tax or company registration details of the seller (if relevant)
· Name and contact details of the buyer
· Date that the product was sent or delivered
· Purchase order number (or similar tracking numbers requested by the buyer
to be mentioned on the invoice)
· Description of the product(s)
· Unit price(s) of the product(s)
· Total amount charged
· Payment terms (including method of payment, date of payment, and details
about charges late payment)
Pro forma invoice (про форма, предварительный счет). In foreign trade, a pro forma invoice is a document that states a commitment from the seller to provide specified goods to the buyer at specific prices. It is not a true invoice, because the seller does not record a pro forma invoice as an accounts receivable and the buyer does not record a pro forma invoice as an accounts payable. A pro forma invoice is not issued by the seller until the seller and buyer have agreed to the terms of the order. In few cases, pro forma invoice is issued for obtaining advance payments from buyer, either for start of production or for security of the goods produced.
Extension
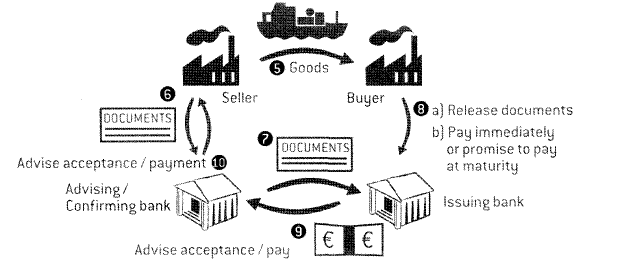
Read about the steps in a transaction involving a letter of credit and put them in the correct order. Use the pictures to help you.
1. Contract
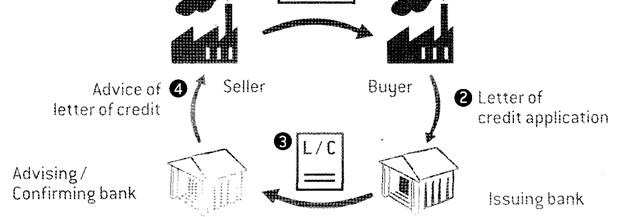
ÿ The advising bank authenticates the letter of credit and sends the beneficiary (the seller) the details. The seller examines the details of the letter of credit to make sure that he/she can meet all the conditions.
ÿ The applicant (the buyer) completes the contract with the seller.
ÿ The issuing bank (the buyer’s bank) approves the application and sends the letter of credit details to the seller’s bank.
ÿ The buyer fills in a letter of credit application form and sends it to his or her bank for approval.
ÿ If the documents are in order, the advising bank sends them to the issuing bank for payment or acceptance.
ÿ The advising bank pays the seller and notifies him or her that the payment has been made.
ÿ The issuing bank advises the advising (or confirming) bank that the payment has been made.
ÿ The issuing bank examines the documents from the advising bank. If they are in order, the bank releases the documents to the buyer, pays the money promised or agrees to pay it in the future, and advises the buyer about the payment. The buyer collects the goods.
ÿ The seller presents the documents to his/her bankers. The advising bank examines these documents against the details on the letter of credit.
ÿ When the seller is satisfied with the conditions of the letter of credit, he/she ships the goods.
Step 6
Дата добавления: 2015-10-28; просмотров: 228 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| Summaries, Notes, Reports | | | Vocabulary bank |