
Читайте также:
|
МЕТОДИЧНІ РЕКОМЕНДАЦІЇ
до самостійної роботи та завдання
з дисципліни «МІКРОЕКОНОМІКА»
(англійською мовою)
для студентів спеціальностей «Банківська справа» та «Облік і аудит»
Денної форми навчання
Харків – 2013
THE GENERAL OVERVIEW OF THE DISCIPLINE
Microeconomics as a component of economic theory studies the behavior and mechanism of decision making by individual economic agents (individuals, households, businesses, organizations and other Microsystems), fulfilling the goals for the available limited resources and which can also be found an alternative use. The focus of Microeconomics is a behavior of consumer and producer and its optimization, market demand and supply, relative prices of goods, allocation of resources for alternative use, partial and general equilibrium and so on.
Purpose of the studying: forming of a market-oriented economic outlook and knowledge about the correct economic choice and evaluate the use of scarce productive resources that constitute multiple-level optimal economic decisions structural elements of the national economy.
Objectives: providing knowledge of basic microeconomics and provision of micro-analysis tools to make rational economic decisions, preparation for the study of applied sciences based on microeconomic theories of perception that business success depends on seed capital and understanding of the principles of functioning economic Microsystems in various market situations and their ability to use effectively.
Subject of the studying: behavior of economic actors and decision-making mechanism for limited productive resources and alternative opportunities for their use.
The main content of the discipline is presented in 14 topics.
Methodological basis of discipline is to analyze the processes of economic development of individual economic entities on the basis of a systematic approach, dialectical method of economic modeling, methods of induction and deduction limit and graphical analysis.
Program of the discipline corresponds strongly to the content and requirements of education and qualification program of Bachelor of area of preparation 6.030508 “Finance and credit” of specialization in “Banking and Finance”, field of knowledge 0305 – “Business and Entrepreneurship”.
QUALIFICATION REQUIREMENTS IN THE FIELD OF KNOWLEDGE WITH DISCIPLINE
Required training base before studying the course
Before studying the course “Microeconomics” students received knowledge, skills and abilities in “Political economy” (amount 5 credits), and “Macroeconomics” (amount 5 credits).
2. As the result of the discipline the student should know:
- which section of economic science should address the choice of alternative uses for scarce resources in the formation of purpose;
- principles of rational behavior of consumers in market conditions;
- methods of optimization of producers in different types of market structures;
- microeconomic prerequisites of equilibrium;
- the terminology and basic means of microeconomic analysis.
3. As the result of the discipline the student should be able to:
- independently perform technical and economic analysis related to the analysis and justification of rational behavior in the micro market conditions;
- analyze the formation of the industry and market demand for resources;
- evaluate the effectiveness of release of goods.
Form of learning: lectures, seminars, self-study and individual work using visual aids, technical training, consultation providing consolidation of theoretical knowledge, and encourages the development of practical skills and creative thinking.
METHODICAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE SELF-WORK ACCORDING TO THE TOPICS OF THE COURSE
The methodical recommendations are presented in the set of the general rules to provide the self-study and in the definite tasks which are helpful in studying the discipline. These materials correspond with the Studying Program of the discipline and the general requirements to studying process at the University.
Since the studying is provided with the different forms of learning (including lectures, seminars, self-study, consultation and individual work) the students have to go through all of them to get ready to pass the exam at the end of the course studying (the final assessment of their knowledge). To help the students in this task there are some useful recommendations and links for every topic.
To master the material of the course it’s needed to read the topics in lecture notes, corresponding topics in the advised and available textbooks on Microeconomics and do the tasks presented in the following set of typical tasks:
1. Theoretical questions that require knowing of basic definitions and laws (for example, fitting the proper word to the gap, giving the definition of the economic phenomenon, matching the definition and the term etc.)
2. The tasks on plotting the graphs with further analysis or explaining the given graphical model
3. Calculations of the economic values on the basis of given economic data and plotting the graphs using the results (to do the task the students have to know the main formulas and the laws on microeconomics). This part can be presented by individual home task, based on some definite data for the calculation. So every student should solve the variant of the task which coincides with his/her number in the list of the group.
4. Analyzing the real situations on consumer and producer behavior, market situations etc.
Module 1. Theory of consumer behavior. Theory of enterprise
Topic 1. The Subject matter and method of microeconomics
(5hours)
Key points:
1. The Subject Matter of Microeconomics. The role of Microeconomics
2. The use and limitation of Microeconomic theory
3. Economic methodology. Microeconomic models
Give the definitions to the following terms:
- Method of study
- Economic agent
- Economic good
- Free good
- Economic resource
- Economic model
- Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
Answer the following questions:
1. What is the subject matter of Microeconomics?
2. Who is economic agent?
3. What is the role of Microeconomics for modern economic agent and the economy of the country?
4. What are the main study methods used in Microeconomics?
5. Provide the economic models you know that can be used in Microeconomics.
6. Define the difference between normative and positive questions
7. Explain the concept of opportunity costs.
Solve the graphical tasks:
1. Draw a PPF for missiles and automobiles, assuming that they utilize similar but not perfectly transferable resources.
List the factors that would shift the PPF.
Indicate how the frontier will be affected by technological improvements in the production of automobiles but not missiles by drawing a second frontier. Be sure to specify the direction of the movement of the PPF, if applicable, with an arrow pointing from the old towards the new PPF.
2. Questions a) to c) refer to the production possibilities frontier shown below.
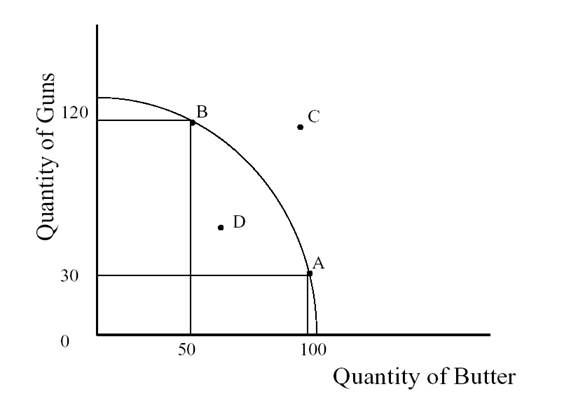
True or false
a). In the graph shown above, at point B, society is producing the maximum possible amount of butter.
b) To move from point A to point B, society would have to cut down on its gun production and increase butter production.
c) Point D is feasible and effective/
d) Point C shows the combination of guns and butter production under much bigger quantity of used resources.
e) Points C and D are ineffective.
3. Assume that the United States contributes disproportionately more resources to the defense of Western Europe than do other NATO allies, and as a consequence these other countries can invest a larger share of their resources in capital and other goods and services. Use production possibilities curves to show both short- and long-run consequences regarding the economies of the United States and Western Europe.
Give a short answer:
1. “Children should learn to clean up after themselves by the age of six.” Is this a positive or a normative statement? __________________________________________________________________
2. “The business sphere contributed 59% of production in the US in 2000.” Is this a positive or a normative statement? __________________________________________________________________
3. List the three basic economic questions.
__________________________________________________________________
4. A family enjoys a three-week vacation. In order to afford this vacation, the family saved money over the course of a year. Was earning this money a final goal or an intermediate goal? Explain why? __________________________________________________________________
5. Technological innovations can vastly increase a society’s productive capacity. How might a technological innovation affect a society’s production possibilities frontier?
__________________________________________________________________
Think on analytical quiz:
1. What is the opportunity cost of your studying at the University? Provide the money value calculation and explain why did you make the decision to study?
2. Assume that France can produce wine at 25 bottles per worker and cheese at 5 pounds per worker. Assume that Italy can produce 10 bottles of wine per worker and 20 pounds of cheese per worker.
a. In terms of cheese, what is the opportunity cost of producing wine in each country?
b. Who has the comparative advantage in producing cheese?
c. Which country should most likely specialize in cheese? in wine?
Дата добавления: 2015-10-26; просмотров: 207 | Нарушение авторских прав
| <== предыдущая страница | | | следующая страница ==> |
| ИСТОРИЯ РОССИИ | | | Topic 2. Marginal utility theory and consumer behavior |